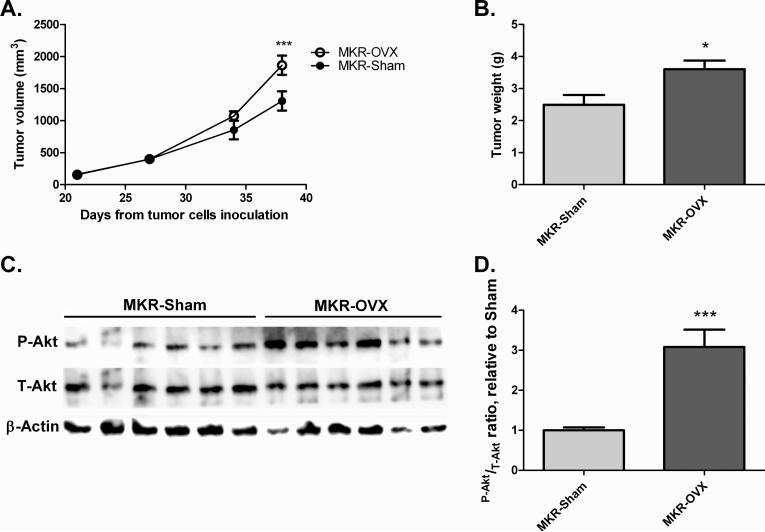
Fig 4. Ovariectomy leads to increased mammary tumor growth in MKR mice and activated Akt signaling in inoculated tumor cells.
Mvt-1 mammary tumor cells (50,000 cells) were inoculated into the mammary fat pad of ovariectomized and sham-operated MKR mice. (A) After detection of tumors, tumor volume was assessed at the indicated times. (B) Tumor weight was measured at sacrifice. (C) Protein was extracted from tumors and Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies directed against phospho-Akt (Thr308, P-Akt), total-Akt (T-Akt), and beta-actin. (D) Densitometry analysis was performed using ImageQuant software. Results are representatives of two independent experiments and presented as mean ± SEM, n=6. Two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison post-test (A), or student's T-test (B,D) were used to determine the statistical significance; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs. MKR-Sham.