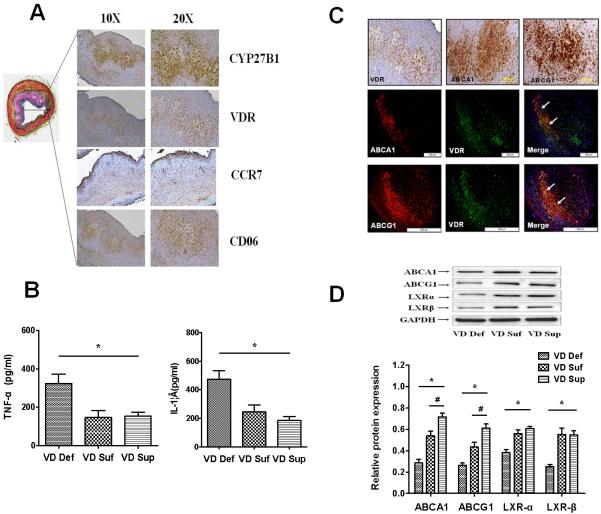
Figure 3. Vitamin D increases cholesterol efflux and M2 macrophage polarization in artery of hypercholesterolemic swine.
Fig.3A: Vitamin D signal-related CYP27B1 and VDR are expressed at sites of M2 macrophage (CD206 positive) foam cells in coronary atherosclerotic lesions of hypercholesterolemic swine (Left= Movat stain, Right = Immunohistochemistry); Fig. 3B: Proteins from the common carotid arteries of different treatment groups of swine were isolated and analyzed to determine the levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β by ELISA. Fig. 3C: ABCA1/ABCG1 are co-expressed with VDR at sites of M2 macrophage foam cells in coronary atherosclerotic lesions of hypercholesterolemic swine; Fig. 3D: Western-blot analysis of ABCA1, ABCG1, LXRα and LXR β expression in the common carotid arteries of different hypercholesterolemic swine. Values are means ± SEM for n=3 animals per group. Statistical differences between groups were detected by one-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, VD Def compared to VD Suf or VD Sup; #p < 0.05, VD Sup or VD Suf, n=3)