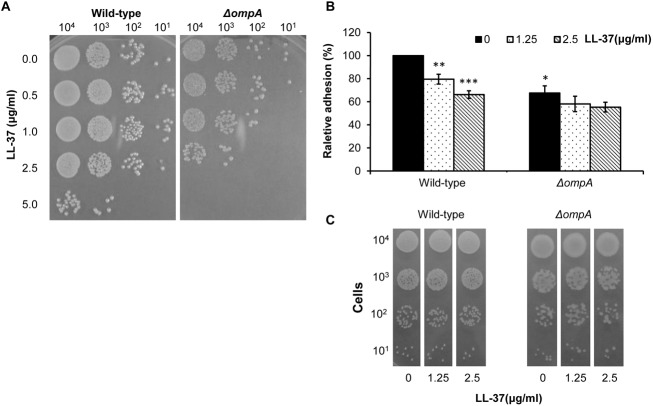
Fig 8. Comparison of LL-37 sensitivity and adhesion ability between the wild type and ΔompA strains.
(A) Sensitivity of the wild-type and ΔompA strains to LL-37 killing was examined using the spot assay. Cells were incubated with different concentrations of LL-37 for 1 hr. Then, the cells were 10-fold serially diluted and spotted onto LB agar plates. The result showed that the ΔompA mutant was more sensitive to LL-37 than the wild type. (B) Cell adhesion of the wild type and ΔompA strains was compared. The wild type and ΔompA cells were attached to polystyrene for 1 hr. Then, non-adherent cells were removed by centrifugation and the adherent cells were stained with crystal violet. The ΔompA mutant showed a decrease in adhesion of 32% compared to the wild type. The adhesion defect in the ΔompA strain was not augmented as obviously as that of the wild type after the addition of LL-37. (C) The spot assay demonstrated that the difference in bacterial adhesion induced by LL-37 was not due to bacterial cell death. The Student’s t-test (**p <0.01) was used to determine the statistical significance of the experimental data.