Fig. 2.
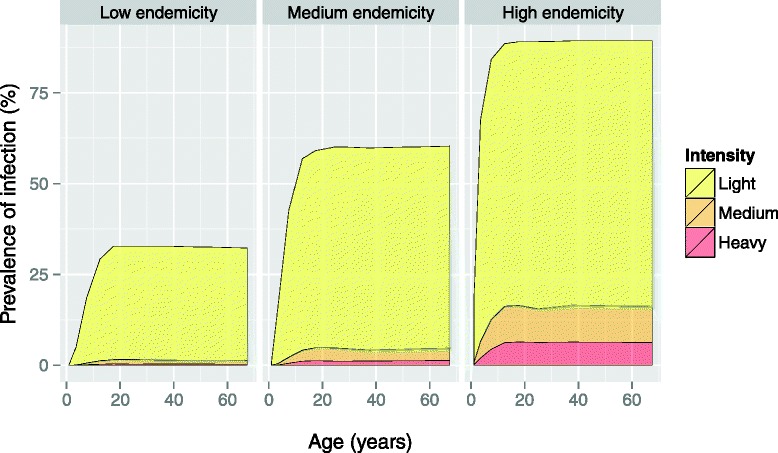
Pre-control distribution of infection intensity (stacked), as predicted by WORMSIM for three endemicity scenarios. The age-pattern is driven by the assumption that host exposure increases linearly from zero to one between ages zero and ten, and is stable from then onwards, resulting in the typical plateau in infection levels from about age 20 onwards [16]. Simulated egg counts are based on single Kato-Katz slides of 41.7 mg with negative binomial sampling error (k Kato-Katz = 0.40, based on an analysis of field data [18])
