Fig. 5.
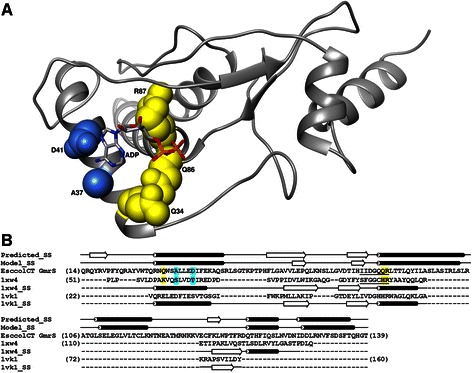
Structural model for the catalytic core of the GmrS domain. a The protein backbone is shown in the ribbon representation. Residues predicted to interact with the phosphate groups of the ligand and with the base are shown in the space-filled representation and colored yellow and blue, respectively. The ADP molecule is colored according to the atom type. The coordinates are available from ftp://genesilico.pl/iamb/models/GmrSD/GmrS.pdb. b Target-template alignment used for comparative modeling of the GmrS domain from the GmrSD CT enzyme. Consensus secondary structure calculated by the GeneSilico metaserver (“Consensus_SS”) and secondary structure of the GmrS model (“Model_SS”) are indicated above the alignment as tubes (helices) and arrows (strands). Secondary structures of the two templates used for modeling (human sulfiredoxin [PDB:1XW4], and ParB-like nuclease from Pyrococcus furiosus [PDB:1VK1]) are indicated below the template sequences. Residues which participate in ATP binding in human sulfiredoxin [56] and their equivalents in the GmrS domain are indicated in blue (adenine binding) and yellow (phosphates binding). Sulfiredoxin signature motif and the most conserved motif of the GmrS domain are underlined
