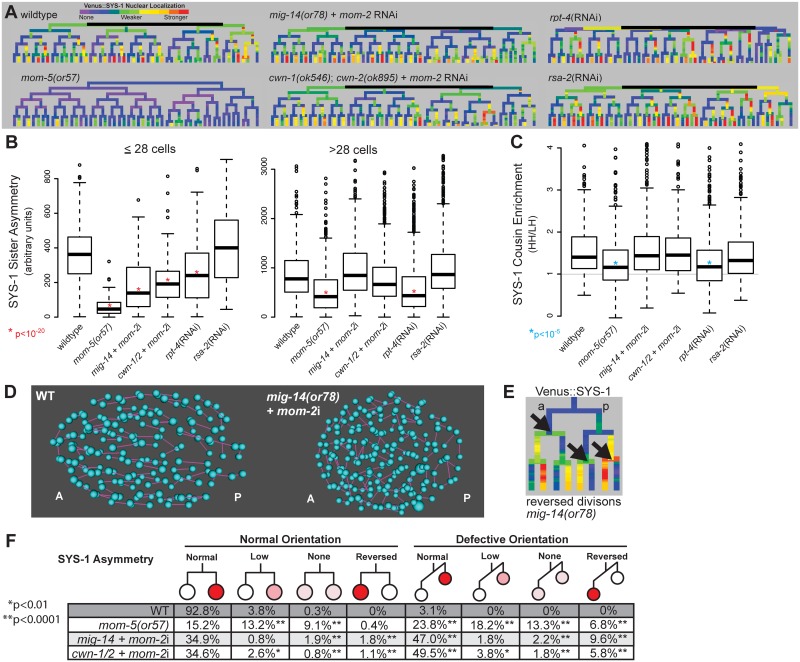
Fig 4. Reduction in Wnt receptor or ligand disrupts nuclear β-catenin asymmetry, cousin enrichment, and division orientations.
A) Lineage trees showing examples of Venus::SYS-1 nuclear localization through the 51 cell stage show that in mom-5(or57) frizzled receptor mutants SYS-1 is completely excluded from the nucleus in virtually all early divisions, while mutations that disrupt Wnt ligand, mig-14(or78) and cwn-1(ok546);cwn-2(ok895) that were treated with RNAi against mom-2, show some divisions with reduced or reversed asymmetry. RNAi against the proteasomal subunit rpt-4 decreases nuclear SYS-1 in some lineages, while RNAi against the centrosome component rsa-2 increases it. B) Boxplots show SYS-1 sister asymmetry is dramatically reduced in early C. elegans Wnt receptor and ligand mutant embryos as compared to wild type (p<10−20, *) and reduced only in mom-5(or57) mutant and rpt-4 RNAi-treated embryos after the 28 cell stage. SYS-1 sister asymmetry is unaffected by rsa-2 RNAi. Edges of the boxes represent the upper and lower quartile, the heavy center line represents the median, the whiskers show the upper and lower bounds, and outliers are shown as circles. C) SYS-1 cousin enrichment (see Fig 3B) is disrupted only in the mom-5(or57) mutant and rpt-4 RNAi-treated embryos. Gray line indicates the SYS-1 cousin enrichment value at which SYS-1 High-High and Low-High cousin nuclear localization are equal (1). D) Division orientations (purple lines) between daughter cells (blue) in wild-type and Wnt ligand mutant embryos at mid-embryogenesis. E) In divisions with reversed polarity (black arrows), the anterior (left) cell has more nuclear SYS-1 than the posterior (right) cell. F) Breakdown of the divisions that have normal or defective orientations and normal, low, none, or reversed SYS-1 asymmetry in wild-type (WT) and Wnt ligand mutant embryos. Total numbers of defective division orientations, cells with reversed polarity and no polarity are significantly different (p<0.0001, **) from wild-type in all three mutant conditions. Divisions with low polarity are also significantly increased for mom-5(or57) and cwn-1/2 + mom-2i.