Fig. 4.
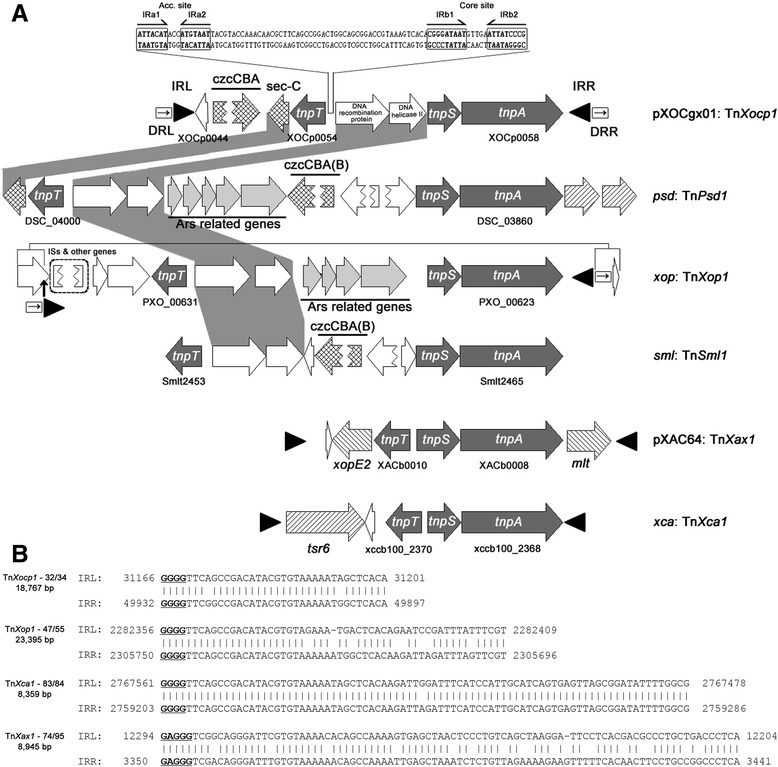
Genetic organizations of the TnXocp1 cassette and IRs sequence analysis. a Genetic organization of the TnXocp1 cassette located in plasmid pXOCgx01 and the alignment with TnXocp1-related structures in other genomes. Genes are indicated by different boxes with the direction of transcription shown by the arrowheads. Three core genes, tnpA, tnpS and tnpT, are shown in dark gray, and passenger genes related to czcCBA cluster in cross stripes, and genes related to arsenic resistance in pale gray, while other passenger genes in diagonal stripes or white boxes. The terminal inverted repeats (IRL and IRR) are shown as black triangles. The terminal direct repeats (DR) are shown as direct arrows in rectangle boxes. No IRs or DRs mean that there are no such sequences in those regions. Two segments with palindromes found in the rst region are supposed to be the Acc. site (17-bp IRa1 and IRa2 segment) for TnpT to bind and the core site (23-bp IRb1 and IRb2 segment) recognized by the TnpS recombinase. b IRs sequences identified from pXOCgx01 and other three tnpA-tnpS-tnpT cassettes. All of them are sharing high sequence similarities to TnXocp1 IRs and begin with GGGG except TnXax1, which begins with GAGG. Abbreviations for genomes with tnpA-tnpS-tnpT cassette: psd, Pseudoxanthomonas spadix BD-a59; xop, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A; sml, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia K279a; pXAC64, Xanthomonas citri pv. citri 306 plasmid pXAC64; xca, Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris B100
