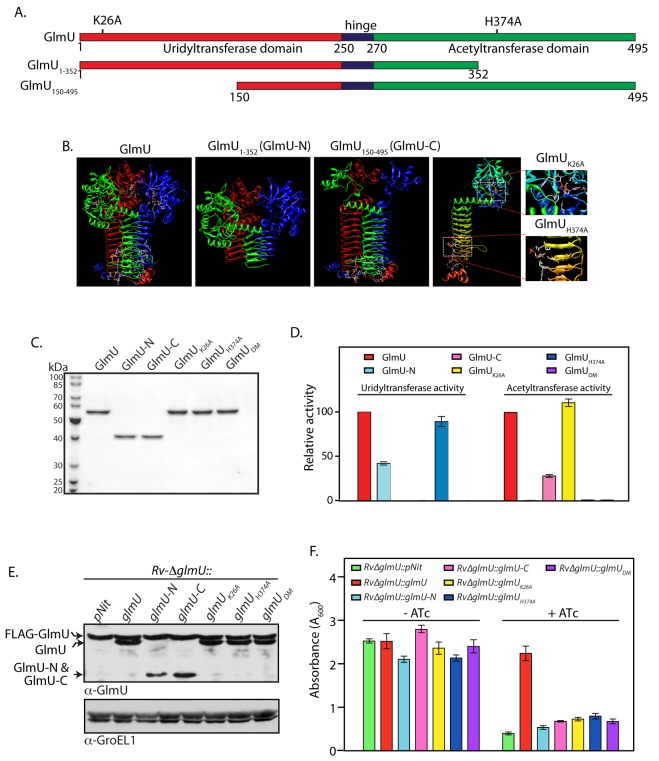
Fig 4. Acetyl and uridyltransferase activities are independently essential.
(A) and (B) Schematic and cartoon representation of GlmUMtb depicting different domains, active site residues and the deletion mutants. (C) GlmUMtb and GlmUMtb-mutants were purified as described earlier [38] and the 1 μg of the purified proteins were resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE and stained with coomassie. (D) Uridyltransferase (left panel) and acetyltransferase (right panel) activities were carried out as describe in Methods using 0.5 to 20 pmoles of wild type or mutant GlmUMtb proteins. Activity was defined as μM product formed / min / pmole of enzyme. Relative activities of the mutants were calculated with respect to the activity of GlmUMtb, which was normalized to 100%. The experiment was repeated three times and the error bars indicate s.e.m. (E) Wild type and mutated GlmUMtb genes were cloned into pNit vector without any N- or C- terminal tag. pNit-glmU wt or pNit-glmU mutant constructs were electroporated into Rv∆glmU, and the WCLs prepared from Rv∆glmU and Rv∆glmU::glmU mutant cultures were resolved and probed with anti-GlmU and anti-GroEL1 antibodies. Bands corresponding to FLAG-GlmUMtb, complemented GlmUwt/mutant and the deletion fragments of GlmU are indicated. (F) Rv∆glmU and Rv∆glmU::glmU mutant cultures were seeded at an initial A600 of 0.1 and grown for five days in the absence or presence of ATc. The experiment was performed in triplicates and the error bars represent s.e.m.