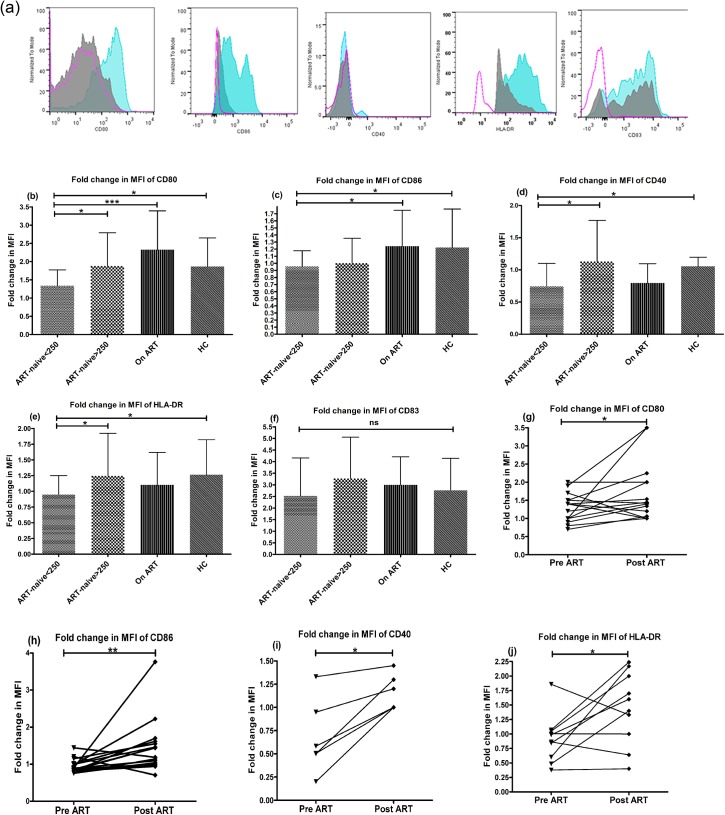
Fig 2. Reduced responsiveness of mDCs of ART-naive patients (CD4+ T-cell counts<250 cells/μL) to LPS-stimulation.
The ability of circulating mDCs to respond to TLR stimulation was assessed using a whole blood DC assay by their abilities to upregulate costimulatory molecules CD80, CD86, CD40, maturation marker CD83 and HLA-DR in response to 5-hour stimulation with LPS (500ng/ml) by flowcytometry in 23 ART-naive patients in advanced stage of disease; 33 patients in early stage of disease, 36 patients on ART and 24 HCs. (a) A representative picture for all markers in a HC subject is shown. The open pink histogram shows the isotype control, solid grey histogram, the unstimulated control and solid blue histogram, the stimulated cells. The fold change in MFI, as a measure of change in expression level of each marker of stimulated mDCs was calculated over the unstimulated mDCs. The HIV-1 infected patients in advanced stage (CD4+ T-cell counts<250) had significantly lower upregulation of (b) CD80, (c) CD86, (d) CD40 and (e) HLA-DR as compared to HCs (p<0.05). (f) The expression of CD83 was not statistically different between the HIV-infected groups and the HCs. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskall-Wallis (KW) test for comparisons between multiple groups with pairwise comparisons using Dunn's multiple comparison adjustment for an overall p values <0.05. Longitudinal analysis of 16 patients pre- and post- 6 months of ART was done by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test and revealed a significant increase in the expression of CD80, CD86, CD40 (n = 6) and HLA-DR (g to j) but not for CD83. Data are represented as mean ± SD. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ns, not significant.