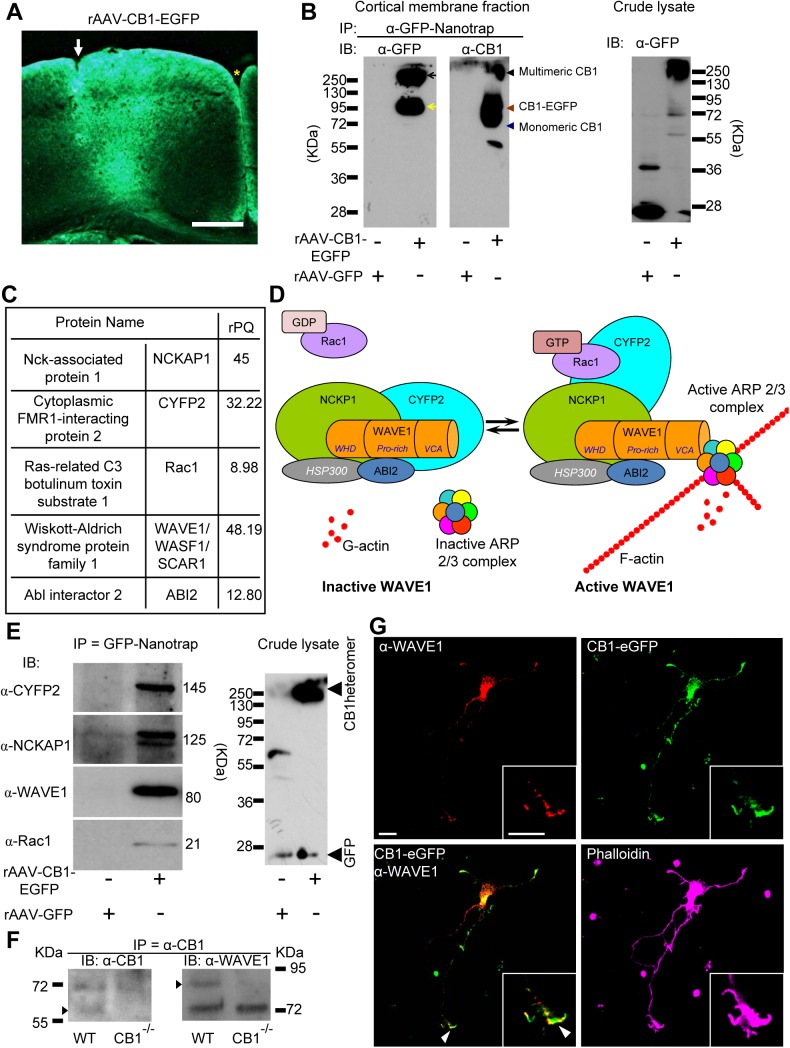
Fig 1. CB1 physically interacts with members of the WAVE1 signaling complex in mouse brain and colocalizes with WAVE1 in neurons.
(A) Expression of EGFP-tagged CB1 (CB1-EGFP) in mouse brain 4 wk after cortical injection of rAAVs. Injection site is marked with a white arrow, and medial longitudinal fissure with a yellow asterisk. Scale bar represents 0.5 mm. (B) Validation of solubilization and pulldown of CB1 by immunoprecipitation using GFP-nanotrap on membrane fractions derived from cortex of mice expressing either CB1-EGFP or GFP alone (as control). Immunoblotting (IB) experiments show that anti-GFP antibody pulls down endogenous CB1 and CB1-EGFP from CB1-EGFP-expressing mice, but not from GFP control mice. The successful pulldown shows the high molecular weight form of CB1 (black arrows), the CB1-EGFP monomer (yellow arrow) and endogenous CB1 (blue arrow head). (C) Summary of MS analysis of GFP nanotrap-immunoprecipitates from the cortex of CB1-EGFP-expressing mice or GFP-expressing control mice (n = 5). rPQ is relative peptide query score. Values for rPQ > 4 indicates specific purification in comparison over negative control. (D) Schematic representation of activation of the WAVE1 complex by GTP-bound (activated) Rac1. (E) Immunoblotting on GFP-nanotrap-immunoprecipitates showing that cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 2 (CYFIP2), NCK-associated protein 1 (NCKAP1), WAVE1 and Rac1 are coimmunoprecipitated with GB1-EGFP, but not with GFP, from the mouse cortex. (F) Immunoblotting on α-CB1-immunoprecipitates showing that WAVE1 is coimmunoprecipitated with CB1 from cortical lysates derived from wild-type mice, but not in lysates from CB1-deficient mice (CB1-/-). (G) Colocalization of WAVE1 and EGFP-tagged CB1 in growth cones (magnified in inset) of developing cortical neurons with pyramidal morphology. The actin cytoskeleton is counterstained with Phalloidin (growth cone magnified in inset). Scale bars represent 10 μm.