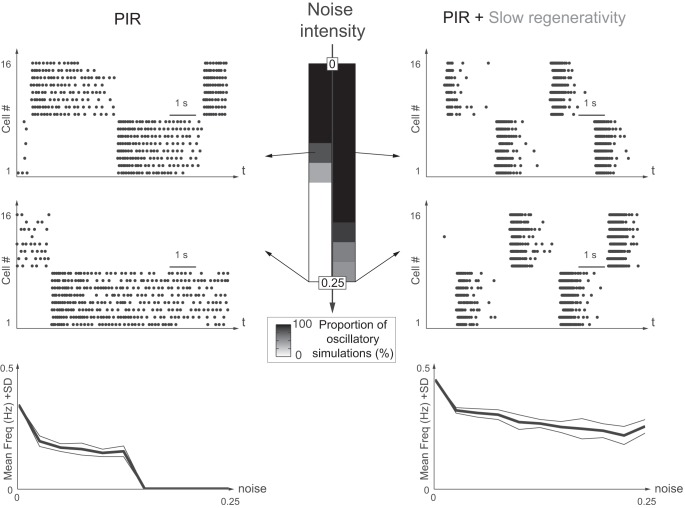
Fig. 7.
Slow regenerativity makes network oscillations robust against exogenous noise. Network oscillations are robust toward exogenous noise only with slow regenerativity. Left: PIR only. Right: PIR + slow regenerativity. Gaussian white noise (noise intensity, D, ranges from 0 to 0.25 mV2) is added to the neurons (see materials and methods for a description of noise). The grayscale code indicates the proportion of simulations with stable rhythmic activity out of 10 simulations. Upper and lower raster plots indicate noise intensity D of 0.10 and 0.25 mV2, respectively. Bottom: plots of the mean frequency (bold line) and 1 SD variation (thin lines) for each noise level for the 10 simulations with oscillations.