Table 1.
Schematic comparisons among various testing methods.
| One-sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methoda | MVT/LME | AUC | L2D | EXC (XUV and XMV) |
| H0 | α1 = … = αm = 0 | α1 + … + αm = 0 | α1 = … = αm | |
| Dimensions in ℝm | 0 | m−1 | m−1 | 1 |
| DFs for F-statisticb | m, n−m−q+1 | 1, n−q | 1, n−q | m−1, (m−1)(n−q) |
| Geometric representationc of H0 and H1 (m = 2) | 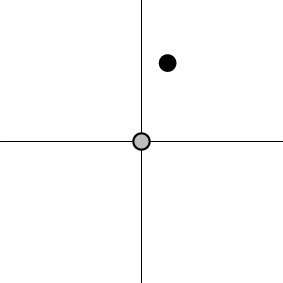 |
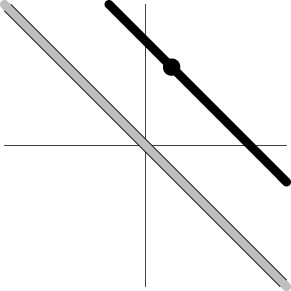 |
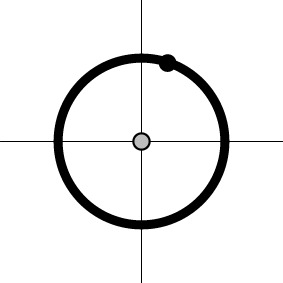 |
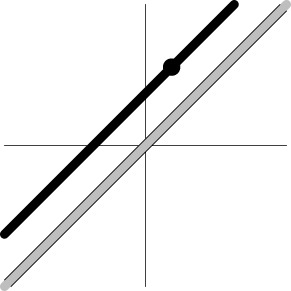 |
| Geometric representationd of HDR when detection failure occurs due to improper H0 formulation | no | 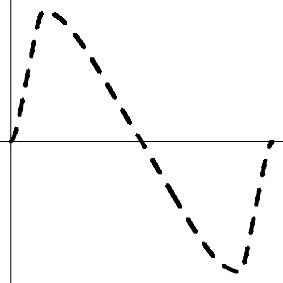 |
no | 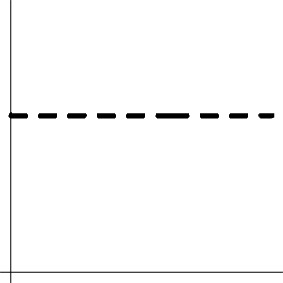 |
| Two-sample or paired | ||||
| Method | MVT | AUC | L2D | EXC (XUV and XMV) |
| H0 | α11 = α21, …, α1m = α2m | α11 − α21 = … = α1m − α2m | ||
| Dimensions in ℝm | 0 | m−1 | m−1 | 1 |
| DFs for F-statistic | m, n−m−q+1 | 1, n−q | 1, n−q | m−1, (m−1)(n−q) |
| Geometric representatione of H0 and H1 | 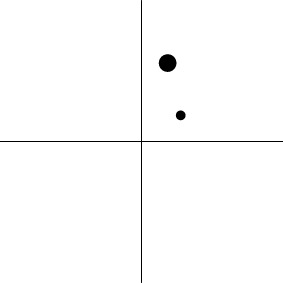 |
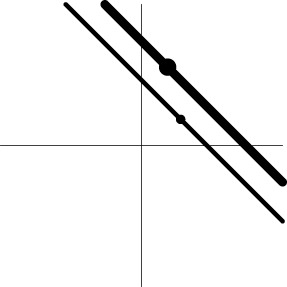 |
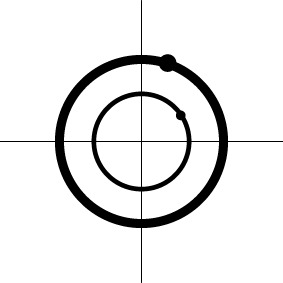 |
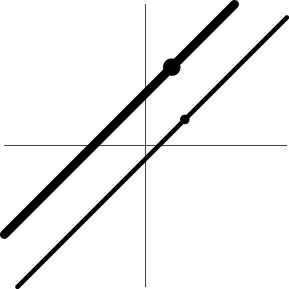 |
| Geometric representationf of HDR when detection failure occurs due to improper H0 formulation | no | 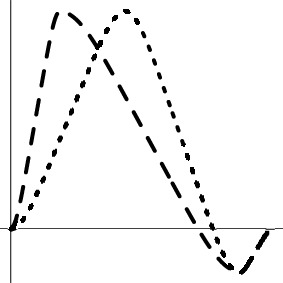 |
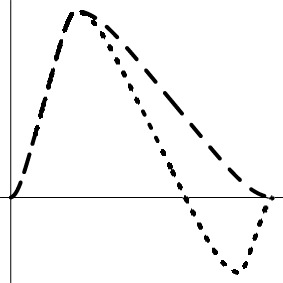 |
 |
The table is meant to show the dimensions of each null hypothesis and an instantiation in the rejection domain while the whole rejection domain is not represented here. For example, the reject region of one-sample Hotelling T2-test for MVT (2a) is outside of an m-dimensional ellipse.
An interesting fact is that the numerator degrees of freedom for the F-statistic under MVT and UVT are the dimensions of the complementary space to the associated null hypothesis H0, or the dimensions of the alternative hypothesis H1.
The two axes represent the two weights associated with the two basis functions. The whole rejection regions are not shown here, and the shaded (gray) and solid (black) areas correspond respectively to the null hypothesis H0 space and an instantiation (and its dimension) in the alternative hypothesis H1 space. Detection failure occurs when the group centroid falls on the diagonal line other than the origin under AUC and EXC.
The horizontal and vertical axes represent time and the amplitude of HDR curve (dashed line).
The two axes represent the two weights associated with the two basis functions. The whole rejection regions are not shown here, and the shaded and sold areas correspond respectively to the null hypothesis H0 space and an instantiation (and its dimension) in the alternative hypothesis H1 space. The two types of line thickness (or dot size) differentiate the two groups (or conditions).
The horizontal and vertical axes represent time and the amplitude of HDR curves. The two line types, dashed and dotted, differentiate the two groups or conditions.
