Figure 1.
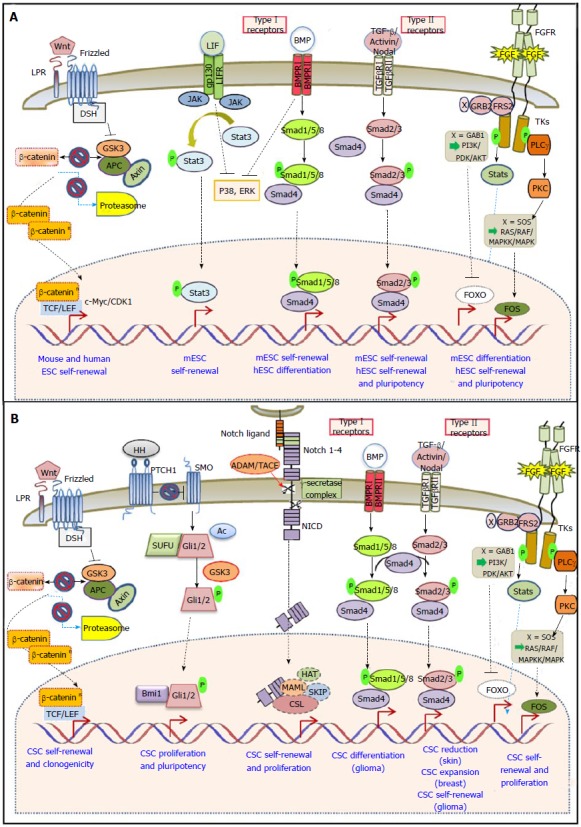
Core signaling pathways in embryonic stem cells and cancer stem cells. A: Mouse ESCs require concerted LIF/BMP signaling to sustain self-renewal and pluripotency, whereas hESC pluripotency depends on the activity of the TGF-β and the FGF pathway. Wnt signaling is important for pluripotency in both species; B: Wnt, Hedgehog, Notch and FGF signaling pathways are associated with CSC self-renewal, while BMP signaling is implicated in CSC differentiation. The TGF-β/Activin/Nodal pathway has a controversial role in CSCs depending on cancer type. ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; CSCs: Cancer stem cells; hESC: Human ESCs; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; Dsh: Dishevelled; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; JAK: Janus-family tyrosine kinase; LRP: Lipoprotein receptor-related protein; PKC: Protein kinase C; SUFU: Suppressor of fused homolog; TCF/LEF: Tcell factor/Lymphocyte enhancer binding factor.
