FIG 1 .
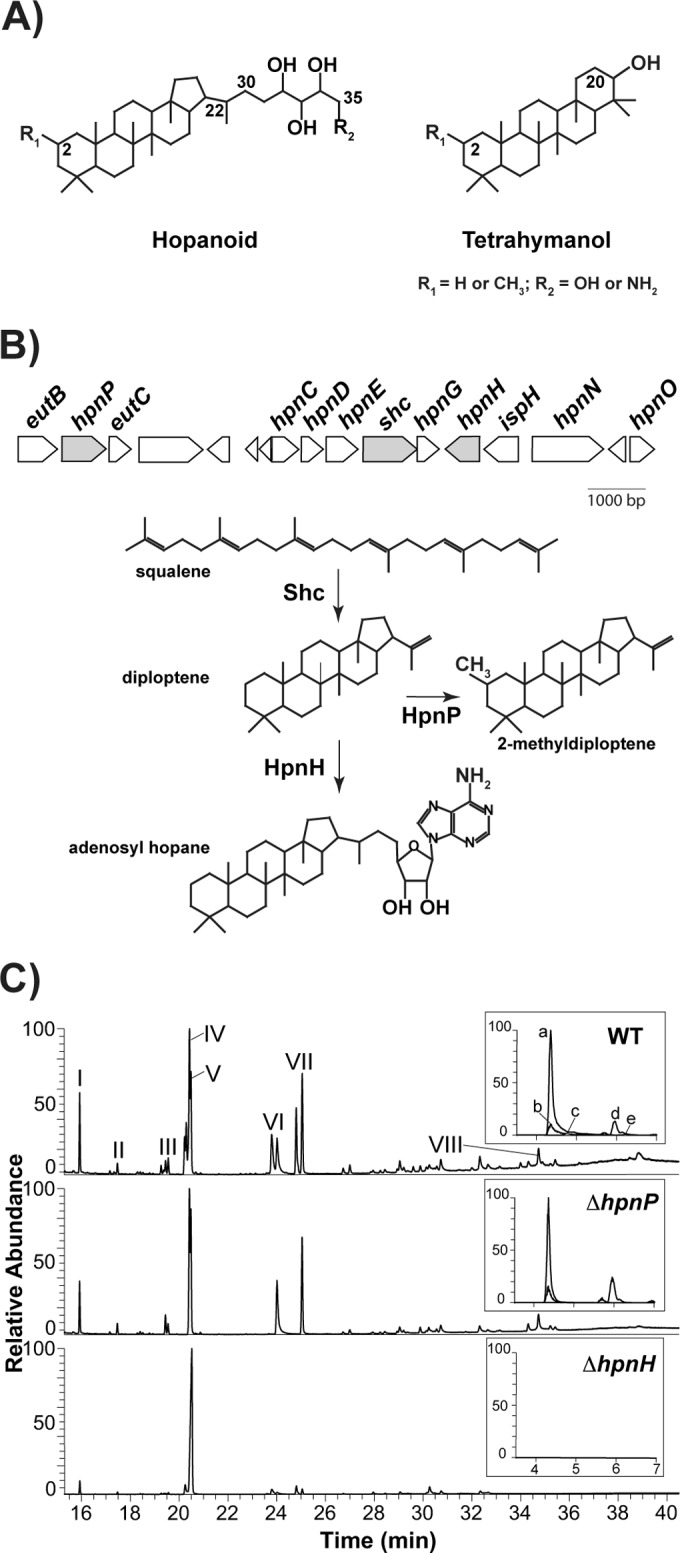
(A) Structures of hopanoid and tetrahymanol. B. diazoefficiens makes C30 hopanoids, such as diploptene (C-22=C-30) and diplopterol (OH at C-22); C35 hopanoids, such as bacteriohopanetetrol (BHT; R2=OH) and aminobacteriohopanetriol (aminotriol; R2=NH2); and tetrahymanol. All these compounds can be methylated at C-2 (2Me, R1=CH3). (B) Hopanoid biosynthetic gene cluster of B. diazoefficiens. In this study, we focused on the genes colored in gray: the shc (squalene hopene cyclase) product catalyzes squalene cyclization to hopene, the first reaction in the hopanoid biosynthetic pathway; the hpnH product catalyzes addition of adenosine to hopene, the first reaction in the synthesis of C35 hopanoids; and the hpnP product catalyzes C-2 methylation. (C) GC-MS and LC-MS (inset) total ion chromatograms of total lipid extracts from aerobically grown B. diazoefficiens strains. For GC-MS, main hopanoid peaks are numbered and the methylated counterparts elute 0.2 to 0.5 min earlier. I, pregnane acetate (standard); II, (2Me) hop-17(21)-ene; III, (2Me) hop-x-ene; IV, (2Me) hop-22(29)-ene (diploptene); V, (2Me) hop-21-ene; VI, (2Me) hopan-22-ol (diplopterol); VII, (2Me and 20Me) tetrahymanol; and VIII, BHP-508. LC-MS: a, aminotriol; b, BHT; c, 2Me-aminotriol; d, adenosylhopane; e, 2Me-BHT. Lipid analysis for each strain was performed in triplicate. For chemical structures of hopanoids, refer to Fig. S1A in the supplemental material.
