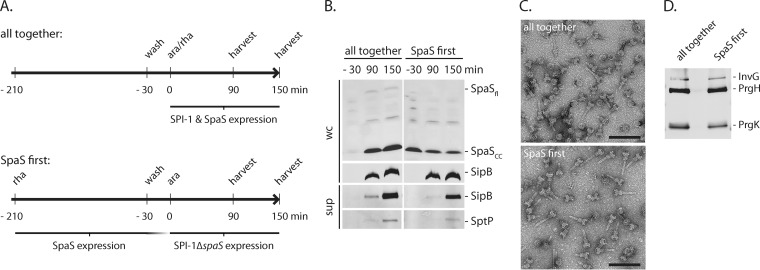
FIG 4 .
Fully functional secretion systems can be obtained from previously provided cleaved SpaS. (A) Illustration of the experimental set up. The experiments were done with Salmonella ΔspaS mutant containing an arabinose-inducible SPI-1 master regulator HilA on the chromosome. C-terminally FLAG-tagged SpaS was complemented from a rhamnose-inducible low-copy-number plasmid. For the assembly control, bacteria were grown for 3 h in the absence of inducing sugars and washed, and expression of SPI-1 and SpaSFLAG was simultaneously induced by the addition of arabinose and rhamnose (ara/rha). To express SpaSFLAG prior to the other needle complex components, bacteria were grown for 3 h in the presence of rhamnose. Then, SpaS expression was switched off by rhamnose removal, and SPI-1 expression (without SpaS) was induced by the addition of arabinose after 30 min, 90 min, and 150 min after SPI-1 induction. SpaS expression and secretion was profiled, and needle complexes were isolated. (B) SpaS expression levels and autocleavage was assayed by SDS-PAGE of whole-cell lysates, subsequent Western blotting, and immunodetection of the FLAG epitope. Likewise, type III secretion into culture supernatants was profiled by immunodetection of the indicated substrate proteins. Abbreviations: wc, whole cells; sup, culture supernatant. (C) Purified needle complexes were negatively stained on copper grids and visualized by electron microscopy. Bars, 100 nm. (D) The protein content of isolated needle complexes was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, Western blotting, and immunodetection of the needle complex base proteins InvG, PrgH, and PrgK.