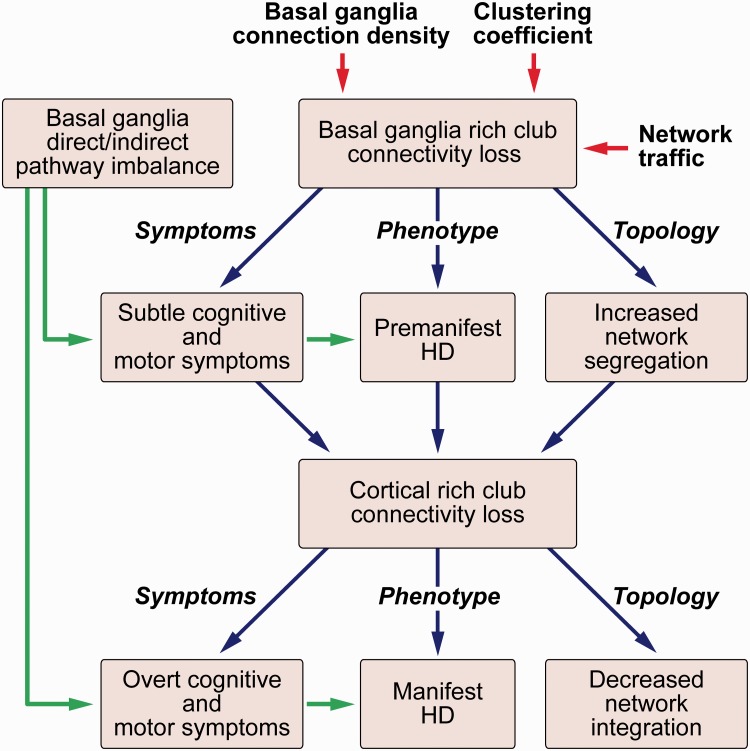
Figure 8.
Summary of findings. There is selective loss of basal ganglia rich club connectivity due to high higher connection to the basal ganglia, higher network traffic and reduced clustering coefficients of rich club regions. This results in increased network segregation leading to the subtle motor and cognitive symptoms seen in premanifest Huntington’s disease. Further loss of cortical rich club connectivity results in reduced network integration resulting in the overt cognitive and motor symptoms seen in manifest Huntington’s disease. HD = Huntington’s disease.