Figure 8. Diagram of the neuroprotective mechanism of tiagabine in MPTP- and LPS-induced PD models.
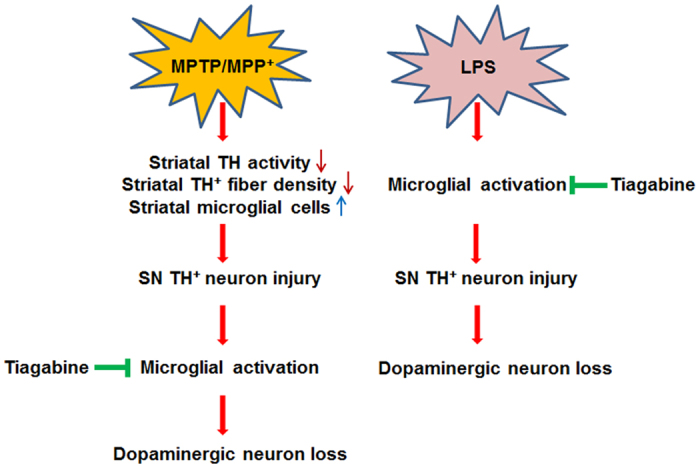
In the left panel, MPP+ (the toxic metabolite of MPTP) causes immediate injury to striatal TH activity and TH+ fibers and the activation of striatal microglial cells. The damage to TH+ neurons and microglial activation in the SN are observed later. Tiagabine inhibits microglial activation and consequently protects dopaminergic neurons. In the right panel, LPS directly stimulates microglia and induces an inflammatory reaction. Tiagabine inhibits this processes and thereby protects against dopaminergic neuron loss.
