Fig. 1. The pancreas' glucose regulatory pathways.
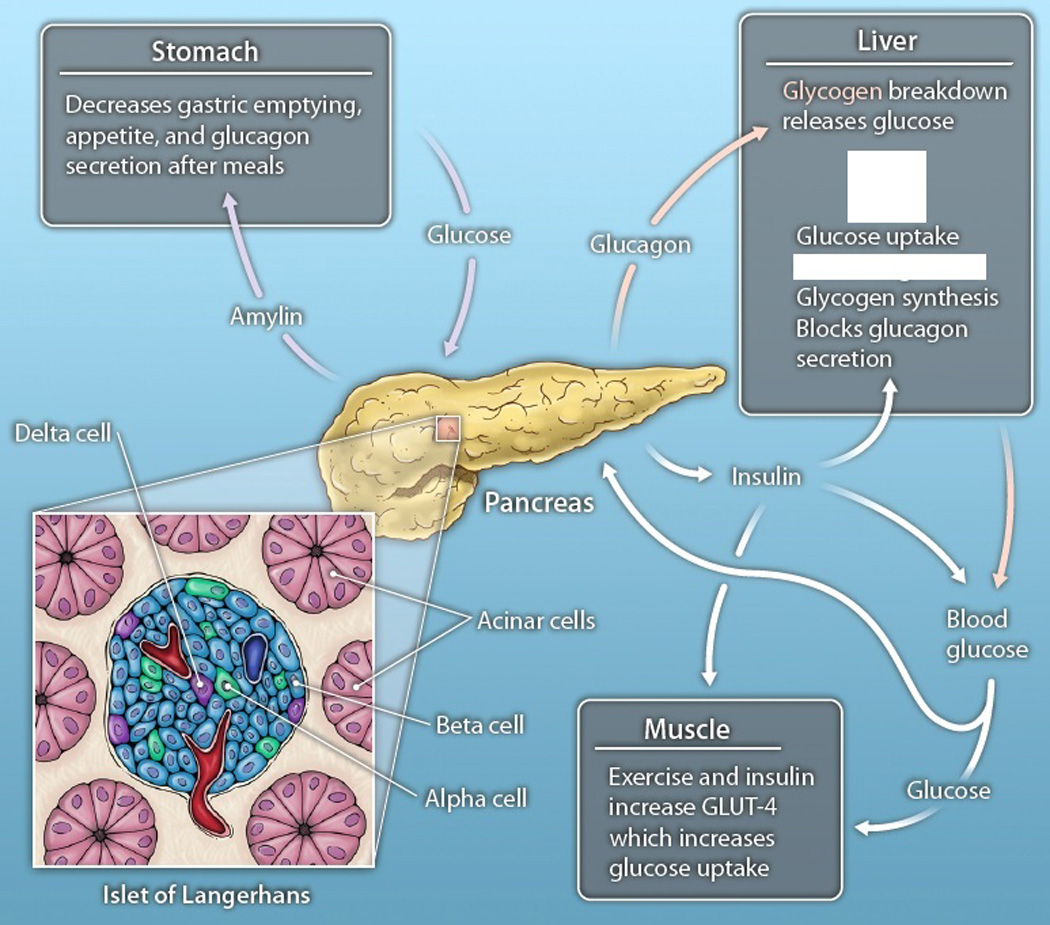
Insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas results in glucose uptake and gluconeogenesis by the liver, upregulation of the GLUT-4 glucose transporter in muscle, and attenuation of glucagon secretion from the islets. Glucagon secreted by the alpha cells stimulates glycogen breakdown by the liver, thereby releasing glucose in times of need. Somatostatin secreted from the delta cells attenuates both insulin and glucagon secretion. Amylin secreted by beta cells delays gastric emptying, decreases appetite, and suppresses glucagon secretion after a meal. Cells within the islets are in close proximity with one another. CREDIT: CHRIS BICKEL/SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE.
