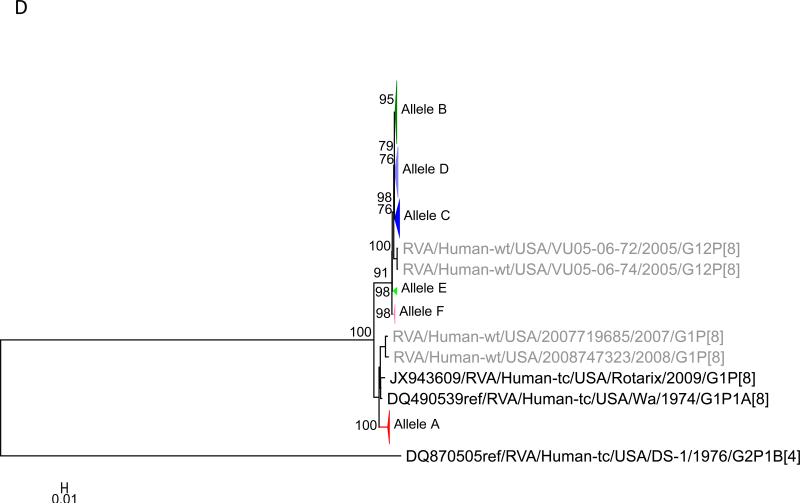
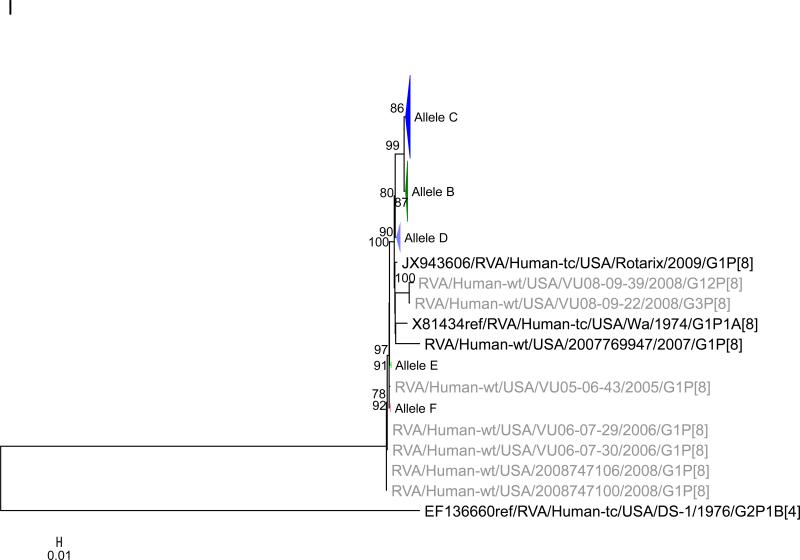
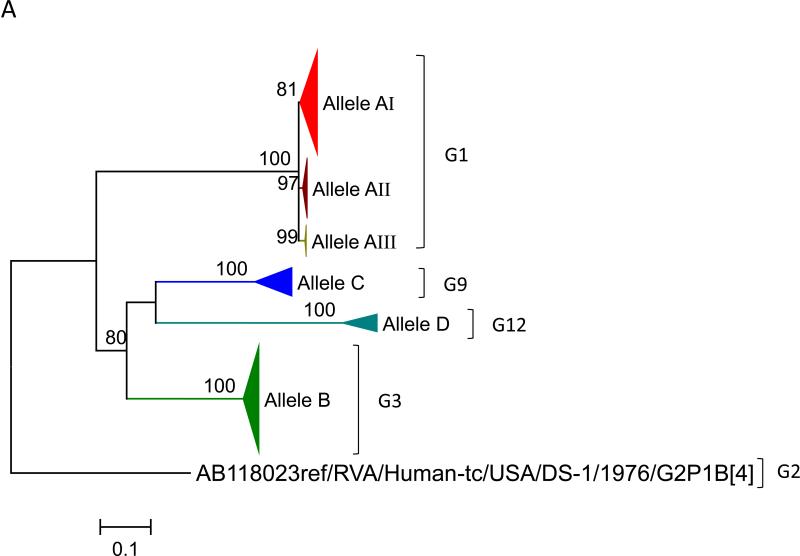
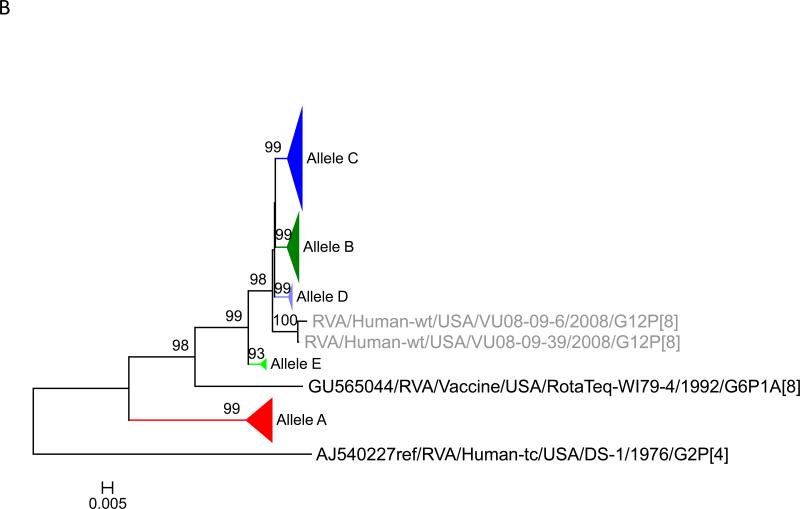
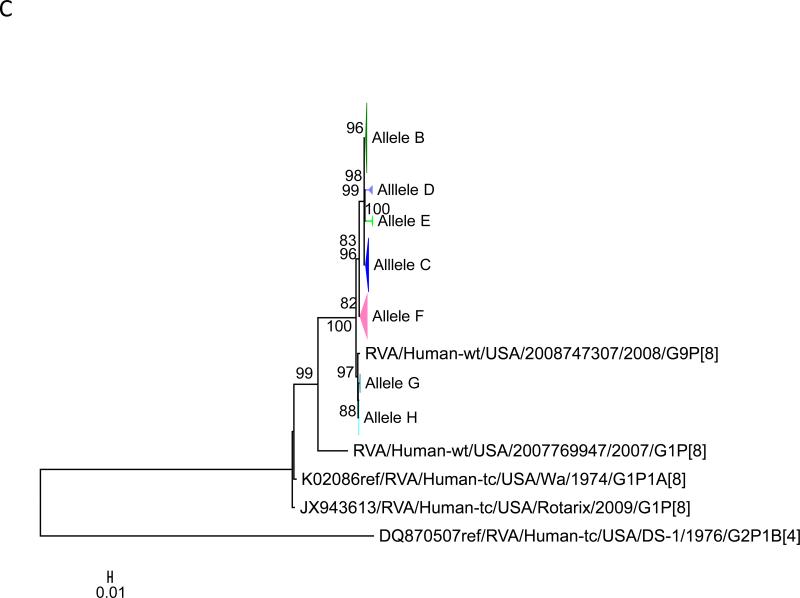
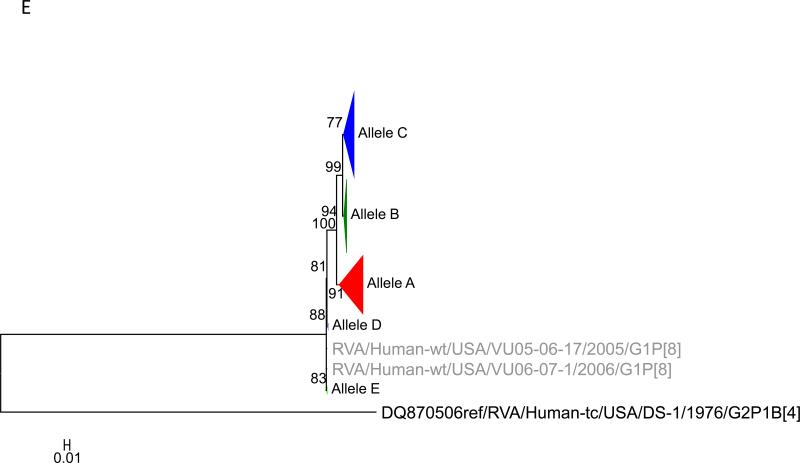
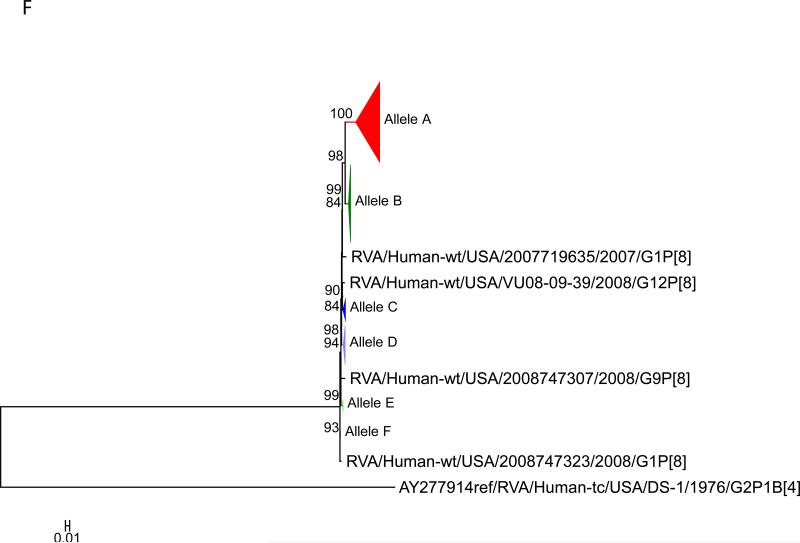
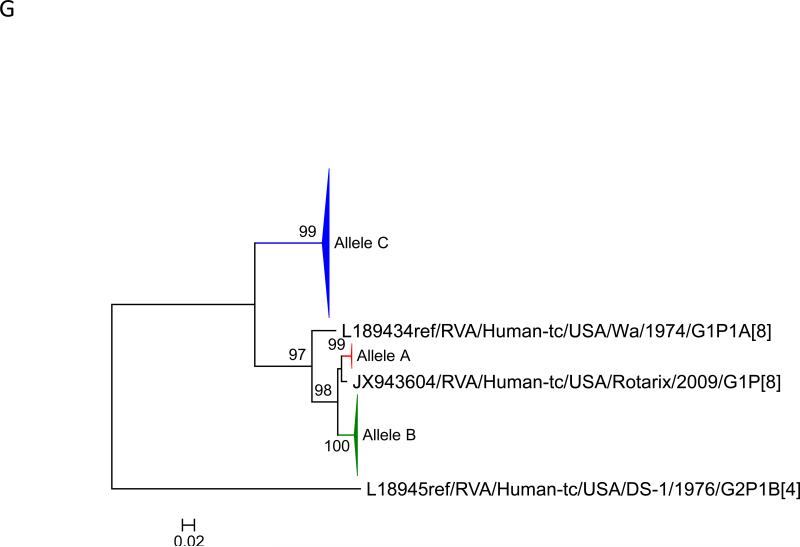
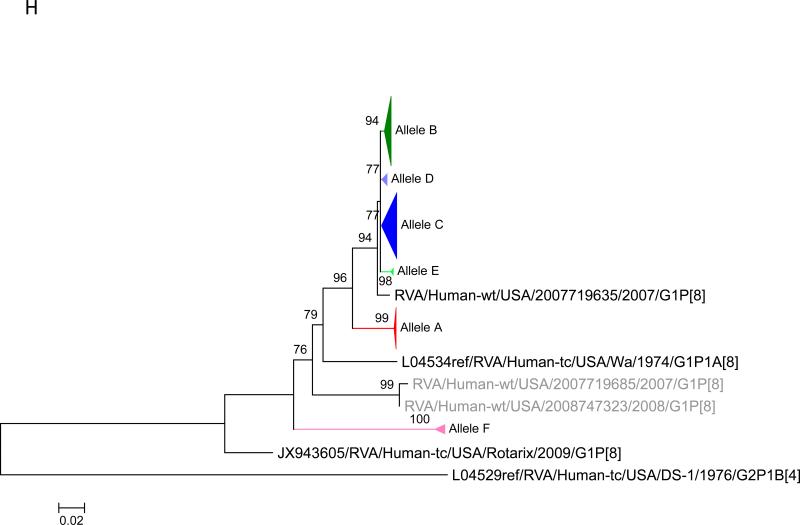
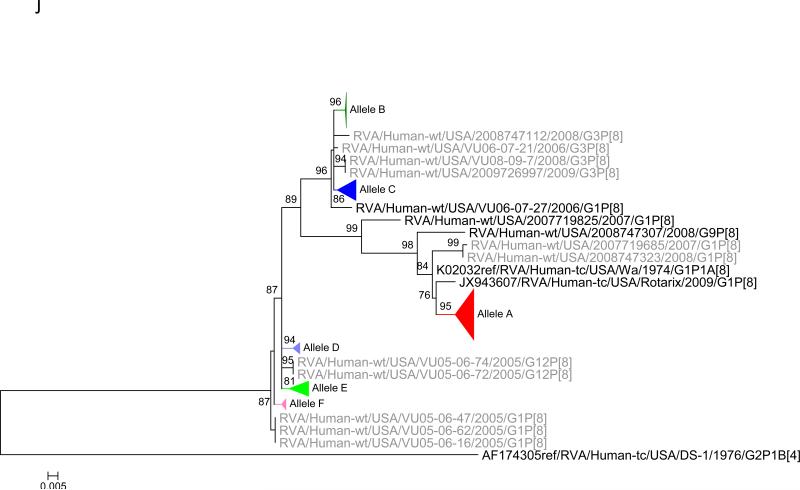
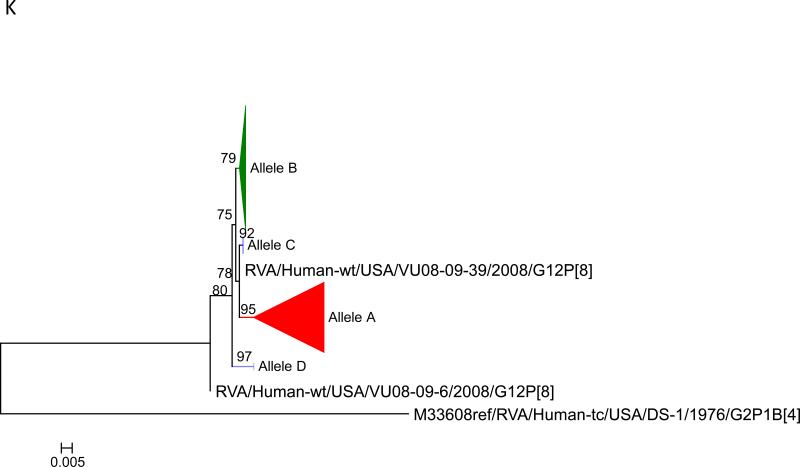
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood trees with aLRT values showing branch support for the 11 RVA genes. The different alleles are colored in red, green, blue, purple, lime, pink, teal and aqua for Alleles A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H respectively. Doublets and singletons are shown in grey and black, respectively (Fig. 1A) VP7. The Allele A in further divided into three clusters: red strains that mostly cluster with G1 (Wa) strains and maroon and olive strains that forms a distinct clusters from the reference Wa Strain. (1B) VP4; (1C) VP6; (1D) VP1; (1E) VP2; (1F) VP3; (1G) NSP1; (1H) NSP2; (1I) NSP3; (1J) NSP4; (1K) NSP5. To see the individual strains comprising each colored triangle, consult the supplemental figures (see supplementary material).