Fig. 2.
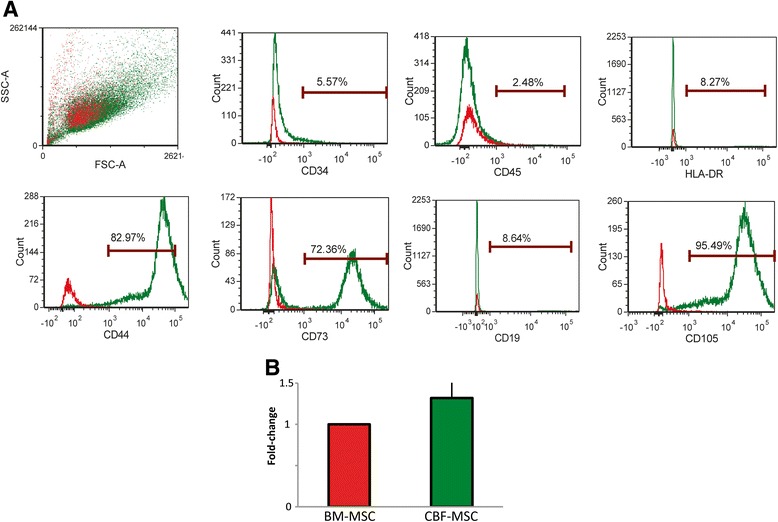
Immunophenotyping characterization. (a) Flow cytometric analysis showing morphological plots for CBF-MSCs soon after isolation (passage 0). Cells obtained from the cortical portion of the bone represent a homogeneous population that stains positively for mesenchymal stem cell-associated markers (CD44, CD73, and CD105) and negative for hematopoietic (CD45 and CD34)- and the major histocompatibility complex-class II (HLA-DR)- or B-lymphocyte antigen (CD19)-associated markers. Stained cells are represented in green, whereas unstained cells seen in red were used as controls. (b) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of RNA expression of the common progenitor-associated marker CD271 in BM- and CBF-MSCs. Data are represented as fold-change compared with BM-MSCs. Values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). BM-MSC bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell, CBF-MSC cortical bone fragment mesenchymal stem cells
