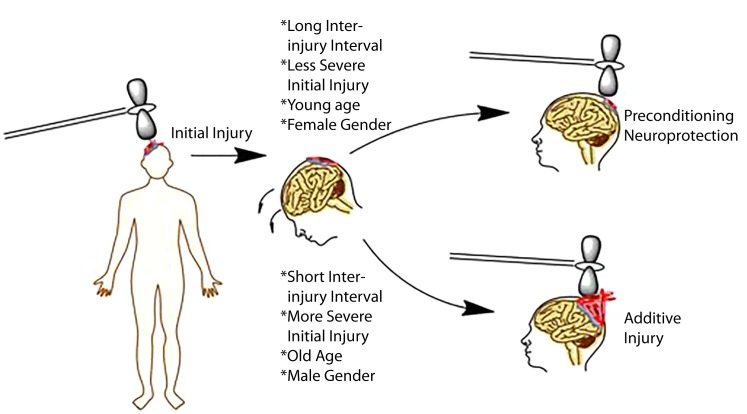
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of factors influencing injury outcomes, particularly in repetitive injury paradigms. Initial evidence indicates that longer inter-injury intervals, less severe initial injury, a younger age, and female gender may serve as protective effects in repeat paradigms. By contrast, shorter intervals, increased severity, older age, and male gender may be associated with worse outcomes.