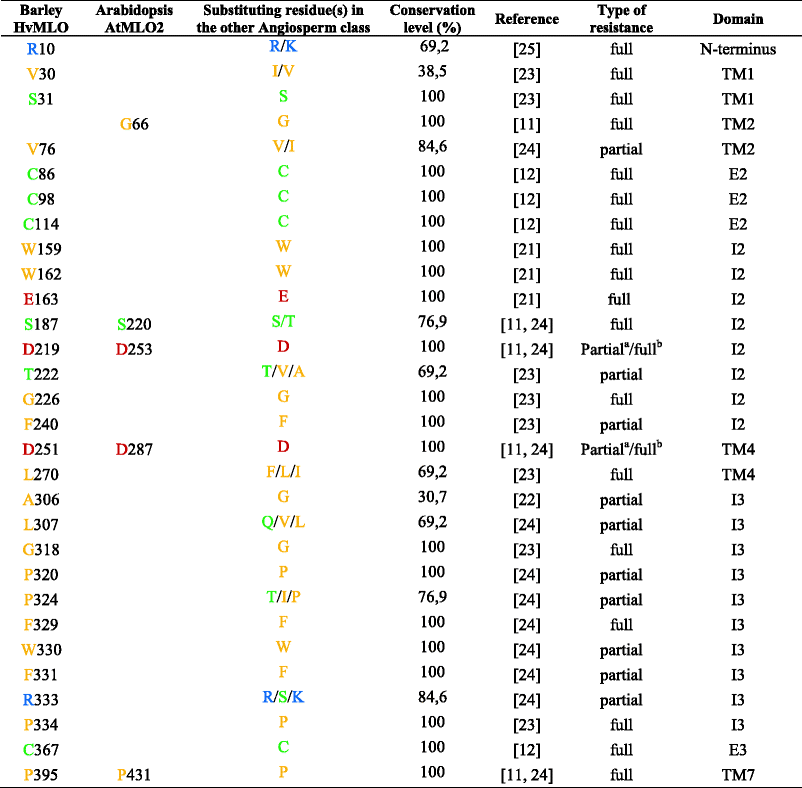
Table 1.
Amino acid residues in dicot AtMLO2 and monocot HvMLO whose mutation has been associated with PM resistance. For each amino-acid, localization in any of the MLO protein domains, including seven transmembrane (TM) regions, three extracellular loops (E), three intracellular (I) loops, the N-terminus and the C-terminus, is indicated
|
ᅟ |
Numbers adjacent to each amino acid indicate their position in either HvMLO or AtMLO2 proteins
Barley and Arabidopsis residues in the same row correspond to each other in HvMLO/AtMLO2 protein alignment
Percentage of conservation is calculated based on the alignment of 13 MLO proteins functionally associated with powdery mildew susceptibility (AtMLO2, AtMLO6, AtMLO12, SlMLO1, CaMLO2, NtMLO1, PsMLO1, LjMLO1, MtMLO1, TaMLO_A1b, TaMLO_B1, OsMLO3 and HvMLO)
Amino acid color is according to its chemical properties: non-polar (yellow), polar, uncharged (green), polar, acidic (red), polar, basic (blue)
apartial resistance observed in barley, bfull resistance observed in Arabidopsis
