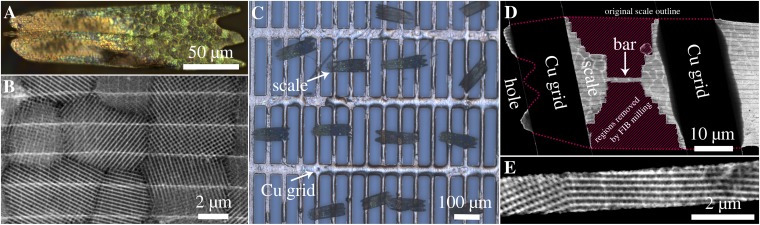
Fig. 2.
Microscopic analysis of microstructure and sample preparation for ET. (A) Light microscopic image (reflection mode) of a single scale comprising differently oriented interconnected nanostructured crystallites, which reflect the incoming light in a varying spectral range and intensity. (B) STEM image of a single scale with several adjacent crystal domains. (C) Light microscopic image of several butterfly wing scales glued onto a Cu grid with rectangular holes. (D) Low-magnification STEM image of a scale after machining a defined bar with several adjacent crystallites by FIB milling. The original scale outline is indicated by the dotted line, whereas the removed regions are dashed in magenta. (E) STEM image of such a typical bar. The distinct contrast in the STEM images is interpreted in local projected mass density, because the solid material consists of amorphous chitin (bright), whereas the pores are unfilled (dark).