Figure 3.
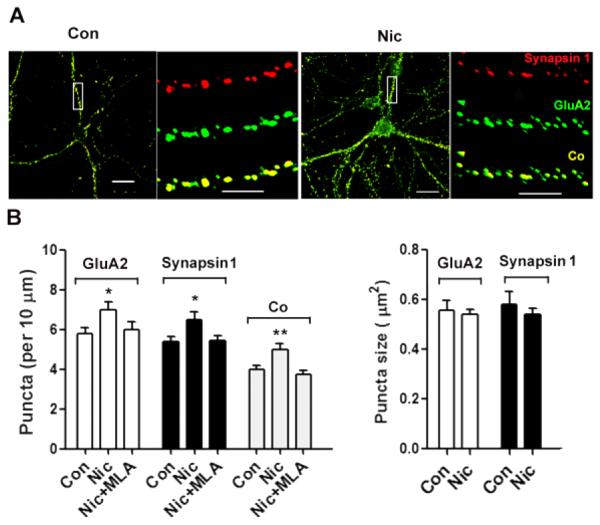
Nicotine, acting through α7-nAChRs, increases surface clusters of GluA2, internal clusters of synapsin1 clusters, and juxtaposition of the two on hippocampal neurons in culture. Neurons were incubated with nicotine for 7 days and then fixed and stained first without permeabilization for GluA2 and then co-stained after permeabilization for synapsin 1. (A) Images showing GluA2 (green), synapsin 1 (red), and co-localization (Co, yellow). Scale bars: 20 μm (left), 5 μm (right) for each set. (B) Quantification of GluA2 puncta number (left) and mean size (right). Including the α7-nAChR antagonist MLA in the 7-day nicotine incubation (Nic+MLA) prevented the nicotine from increasing either GluA2 or synapsin 1 puncta, or altering their co-localization. GluA2, *p ≤ 0.02; synapsin 1, *p ≤ 0.02; Co, **p ≤ 0.01; n = 20 for Con, 22 for Nic, 18 for Nic+MLA.
