FIG 8.
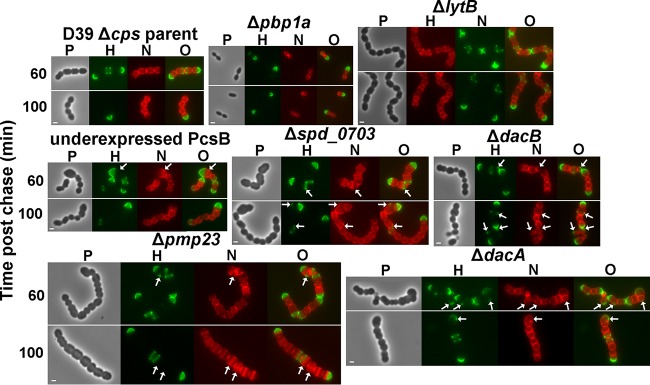
Mutants deficient in PG hydrolases retain hemispheres of stable PG and show regions of inert PG at aberrant division points. Strains IU1945 (D39 Δcps parent), IU6647 (Δpbp1a), IU3877 (ΔlytB), IU2336 (PcsB underexpression [40]), IU3881 (Δspd_0703), IU3880 (ΔdacB), IU3875 (Δpmp23), and IU7204 (ΔdacA) (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) were grown exponentially in BHI broth, labeled with HADA (pseudocolored green; old PG), washed, and chased in the presence of NADA (pseudocolored red; newly synthesized PG) as described in the legend to Fig. 2 and in Materials and Methods. Live cells were imaged by epifluorescence phase-contrast microscopy at the indicated time points after the removal of HADA (chase) and the addition of NADA. Additional time points for each strain are shown in Fig. S6. Minimal variation in labeling patterns was observed for >190 individual cells in diplococci or chains examined for each strain in microscopic fields at different time points after the start of the chase/NADA labeling in two biological replicates, and representative images are shown. Scale bar = 1 μm. P, phase-contrast image; H, HADA labeling (old PG); N, NADA labeling (new PG synthesis); O, overlay of H and N images. Arrows indicate regions in kinked chains bounded by green spots of inert peptidoglycan, by red spots or regions of newly synthesized PG trapped between regions of inert green PG, or by closely spaced red regions of newly synthesized PG. See the text for additional details.
