FIG 3.
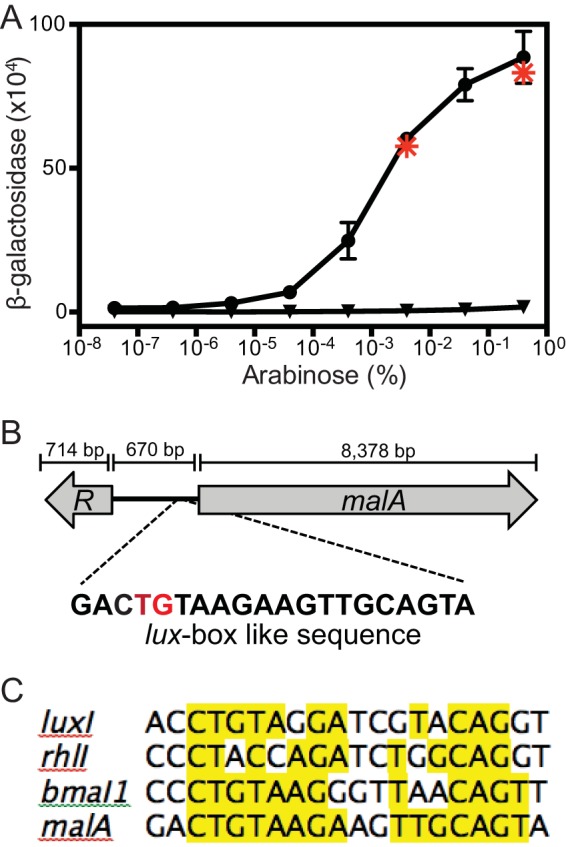
Expression of malA requires MalR and an intact lux box-like sequence in recombinant E. coli. (A) Activation of the malA promoter in E. coli containing an arabinose-inducible malR expression vector (pJN105.malR) and a lacZ reporter with either the wild-type malA promoter (pQF50.PmalA) (circles) or the malA promoter with the T4C and G5A base substitutions (pQF50.mutPmalA) (triangles). The values are the means ± ranges of the results of two independent experiments. Asterisks, E. coli containing pJN105.malR and pQF50.PmalA grown with 0.4 or 0.004% arabinose and 5 μM (each) C8-HSL, 3OHC8-HSL, and 3OHC10-HSL (the B. thailandensis AHLs). Similar results were obtained with 5 μM C4-, C6-, C10-, C12-, C14-, 3OHC6-, and p-coumaroyl-HSL. (B) malR-malA B. thailandensis genomic region. The putative lux box-like element is centered 63.5 bp upstream of the malA translation start site. The red letters indicate the T4C and G5A base substitutions in pQF50.PmalA. (C) Alignment of the malA lux box-like sequence with the lux boxes from Vibrio fischeri luxI, P. aeruginosa rhlI, and B. mallei bmaI1.
