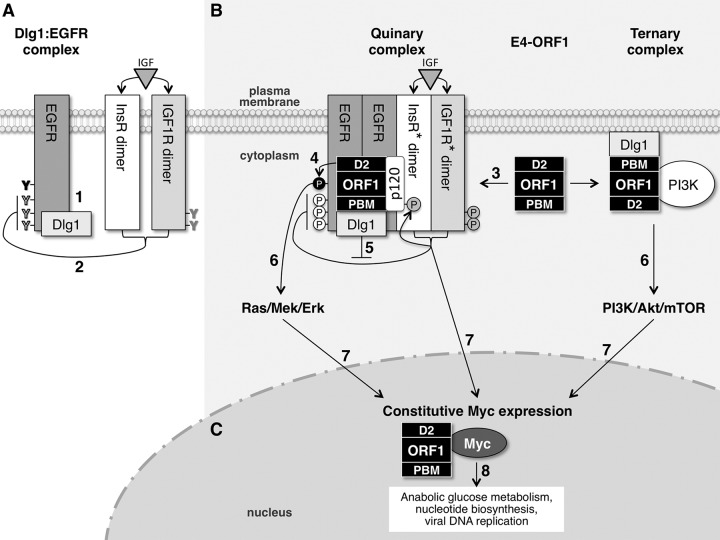
FIG 8.
Hypothesized model for E4-ORF1-induced constitutive Myc protein expression mediated by EGFR, InsR/IGF1R, and PI3K. (A) In normal MCF10A cells, EGFR and Dlg1 form a Dlg1:EGFR complex at the plasma membrane. When activated by ligand, EGFR autophosphorylates tyrosine (Y) residues that directly mediate Ras/Mek/Erk signaling (black) and also those that augment Ras/Mek/Erk signaling (white). InsR/IGF1R activated by ligand specifically downregulates EGFR autophosphorylation on white Y residues that augment Ras/Mek/Erk signaling. (B) E4-ORF1 assembles two different protein complexes at the plasma membrane to activate three separate signaling pathways. E4-ORF1 forms the E4-ORF1:Dlg1:EGFR:InsR:IGF1R quinary complex by binding to the Dlg1:EGFR complex and promoting EGFR dimerization and EGFR association with InsR and IGF1R. In the quinary complex, the E4-ORF1 D2 element promotes EGFR autophosphorylation on black Y residues to activate Ras/Mek/Erk signaling, whereas the E4-ORF1 PBM via binding to Dlg1 enhances the latter signaling by antagonizing InsR/IGF1R-mediated suppression of EGFR autophosphorylation on white Y residues. An additional consequence of E4-ORF1 forming the quinary complex is activation of InsR/IGF1R (denoted by asterisks) and undetermined downstream signaling pathways. E4-ORF1 also binds both Dlg1 and PI3K to form the Dlg1:E4-ORF1:PI3K ternary complex, which activates the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. (C) The three signaling pathways (Ras/Mek/Erk, InsR/IGF1R, and PI3K/Akt/mTOR) activated by E4-ORF1 converge in the nucleus to promote constitutive Myc expression, which enhances Ad replication by ensuring the formation of sufficient quantities of E4-ORF1:Myc complexes to stimulate anabolic glucose metabolism and nucleotide biosynthesis. See the text for details about steps 1 to 8 in the model.