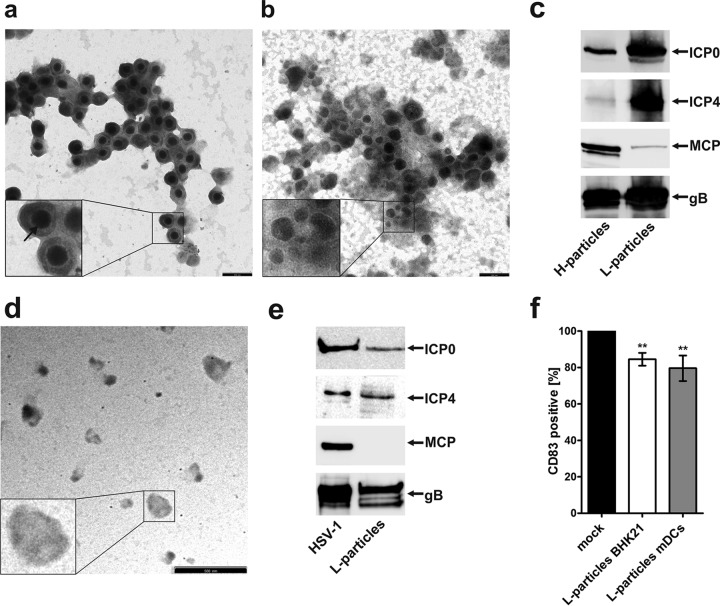
FIG 6.
CD83 downmodulation in HSV-1-negative bystander DCs is mediated by L particles. H and L particle preparations were analyzed by electron microscopy and further characterized using Western blot analysis. Viral particles were isolated using a Ficoll gradient and dialyzed against 20 mM HEPES buffer. (a and b) For electron microscopy, H particles (a) as well as L particles (b) were made to adhere to carbon-coated grids and stained using 1% uranyl acetate and lead citrate. Two independent preparations were analyzed by electron microscopy, and representative data are shown. The insets show particles that have been enlarged 2.5-fold. The arrow indicates the viral capsid. Bars (a and b), 250 nm. (c) H and L particles were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of ICP0, ICP4, MCP, and gB. Three independent preparations were analyzed, and representative data are shown. (d) Electron microscopy analyses of L particles isolated from HSV-1-infected DC supernatant are shown. Bar, 500 nm. (e) L particles derived from mDCs were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of viral proteins. As a positive control, BHK-21-derived virus was used. (f) Mature DCs were left untreated (black bar) or treated with UV-inactivated L particles derived from BHK-21 cells (white bar) or from DCs (gray bar). After 20 h, cells were harvested, and CD83 surface expression was analyzed by flow cytometry. Untreated controls were set to 100%, and relative surface expression is shown. The experiment was performed at least five times with cells from different healthy donors. Significant changes are indicated by asterisks (P < 0.01).