Figure 2.
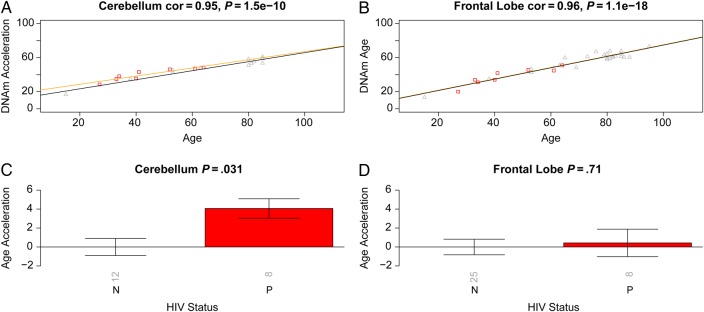
Validation brain data from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected subjects (cases) and HIV-uninfected subjects (controls). Analogous to Figure 1, we used independent data sets (data 2 and 3) to relate HIV status to epigenetic age acceleration in the frontal lobe and cerebellum of cases and controls. A and B, DNA methylation (DNAm) age versus chronological age in cerebellum (A) and frontal lobe (B) samples. Points (subjects) are colored by HIV status: cases correspond to red squares. The orange and black lines depict regression lines case and control samples, respectively. The measure of age acceleration is the same as used in Figure 1. C and D, Age acceleration versus HIV status in cerebellum (C) and frontal lobe (D) specimens. Each bar plot reports the Kruskal–Wallis (nonparametric) group comparison test P value and 1 standard error around the mean. Abbreviation: cor, correlation.
