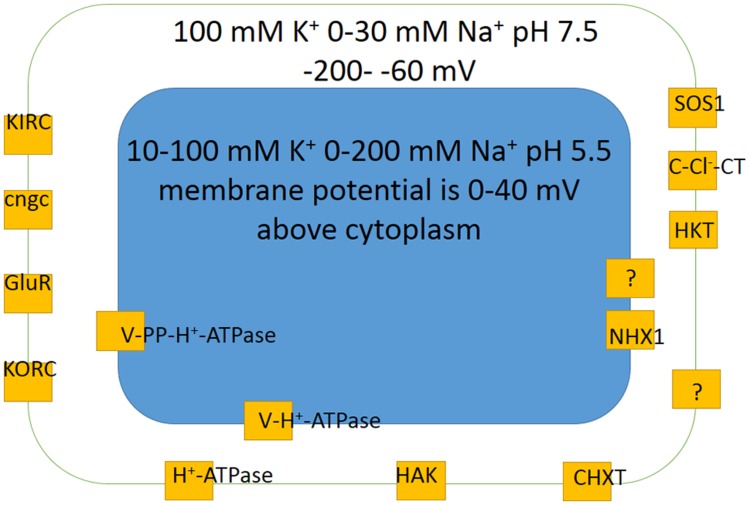
FIGURE 6.
Basic scheme of membrane potentials, potassium K+ and sodium Na+ concentrations and pH values in a generalized plant cell together with main ion transport systems ensuring potassium and sodium transport according to electrochemical forces. Different cell types usually have less transporters, though specialized for more determined ion transport functions. The concentrations and membrane potentials are rather indicative and change depending on conditions of mineral nutrition and are not the same for different cell types (see text and references for more details). KIRC are inward rectifying potassium channels (e.g., Hirsch et al., 1998); KORC are outward rectifying potassium channels; GluR are glutamate receptors; cngc are cyclic nucleotide gated ion channels; HAK is high affinity potassium transporter; CHXT are cation H+ exchange transporters (e.g., Evans et al., 2012); HKT are high K+ affinity transporters; C-Cl--CT are cation chloride contrasnporters; SOS1 is well studied sodium-proton antiporter; H+-ATPase is proton pump of plasma membrane; V-H+-ATPase is vacuolar proton pump; V-PP-H+-ATPase is vacuolar pyrophosphatase, another vacuolar proton pump; NHX1 is vacuolar sodium (cation)/proton antiporter. For more details and description see text.