Figure 1. cGAS and other receptors of cytosolic DNA activate IFNβ transcription via activation of STING.
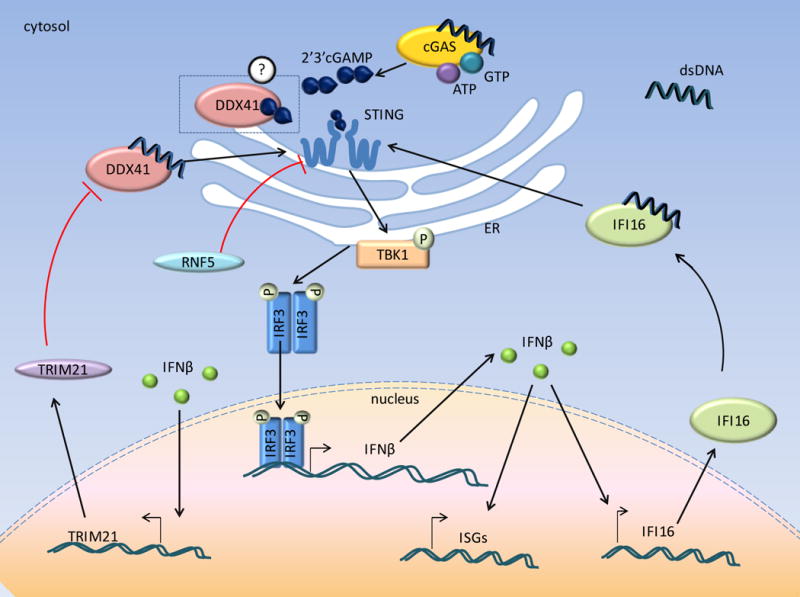
Cytosolic dsDNA binds cGAS and generates 2′3′cGAMP from the substrates ATP and GTP. 2′3′cGAMP in turn binds to and activates the STING dimer. This leads to phosphorylation of TBK-1, IRF3 which are translocated to the nucleus and activate IFN-β transcription. In addition, other receptors, such as, DDX41 and IFI16 also bind to cytosolic dsDNA and lead to IFN-β induction via the common STING pathway. IFN-β in turn induces expression of ISGs including IFI16. Different cytosolic receptors of dsDNA might be cell-type specific or specific to the stage of IFN-β induction.
