Figure 5.
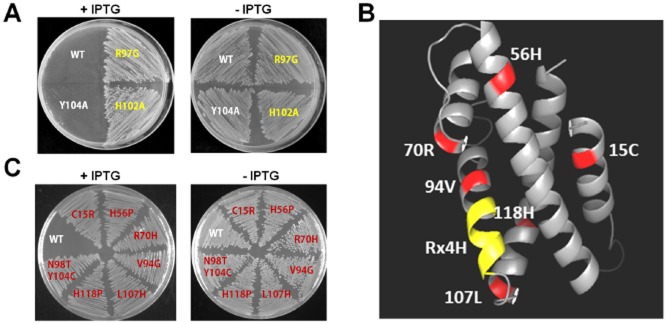
Key residues for determining SO_3166 toxicity. (A) Toxicity results of single-site mutagenesis of the R and H in Rx4H region and an adjacent tyrosine of toxin SO_3166 in the pCA24N-SO_3166 plasmid in DH5α. (B) Predicted 3-D structure of SO_3166. The conserved domain Rx4H is situated at the end of one helix (yellow). Other residues obtained by epPCR assay that affected SO_3166 toxicity are shown in red. (C) Toxicity test of seven strains expressing different mutated SO_3166 proteins obtained by epPCR. WT indicates the wild-type SO_3166 protein; the remainders are mutated proteins. The number in the mutated protein indicates the position of the amino acid in SO_3166. Overnight cultures were streaked on 30 μg/mL chloramphenicol LB plates with or without 0.5 mM IPTG. Two independent cultures were evaluated for each; only one representative image is shown here.
