Figure 11.
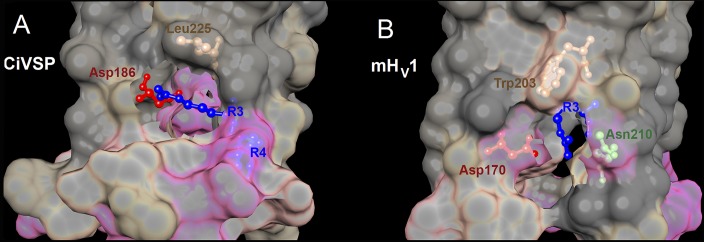
Crystal structures of CiVSP in the “down” state and mHV1 chimera in the closed state reveal pockets that enclose electrostatic interactions involving R3. The crystal structures of the down state of CiVSP (A) (Li et al., 2014) and the closed mHV1 chimera (B) (Takeshita et al., 2014) were superimposed with the same orientation. The top is toward the extracellular surface, and the view is from the side. The interfacial surface between protein and lipid is cut away to show the pocket containing R3 and its interacting partners. Local hydrophobicity is indicated by gray (hydrophobic), tan (intermediate), and pink (hydrophilic). (A) In the down structure of CiVSP (Protein Data Bank [PDB] accession no. 4G80), which is more closely related to HV1 phylogenetically than is the VSD of other ion channels (Smith et al., 2011), R3 faces away from the center of the VSD. The guanidinium group of R3 forms a salt-bridge with Asp186. (B) In the closed structure of mHV1 (PDB accession no. 3WKV), Trp203 and R3 both face away from the center of the channel; the guanidinium of R3 appears to point nearly directly away from the center of the channel. In the mHV1 structure, Trp203 forms the roof of the pocket, in which R3 interacts both with Asp170 (equivalent to Asp174 in hHv1 and Asp186 in CiVSP) and with Asn210. Molecular graphics and analyses were performed with the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), Chimera package (resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics, UCSF, San Francisco; supported by NIGMS P41-GM103311) (Pettersen et al., 2004).
