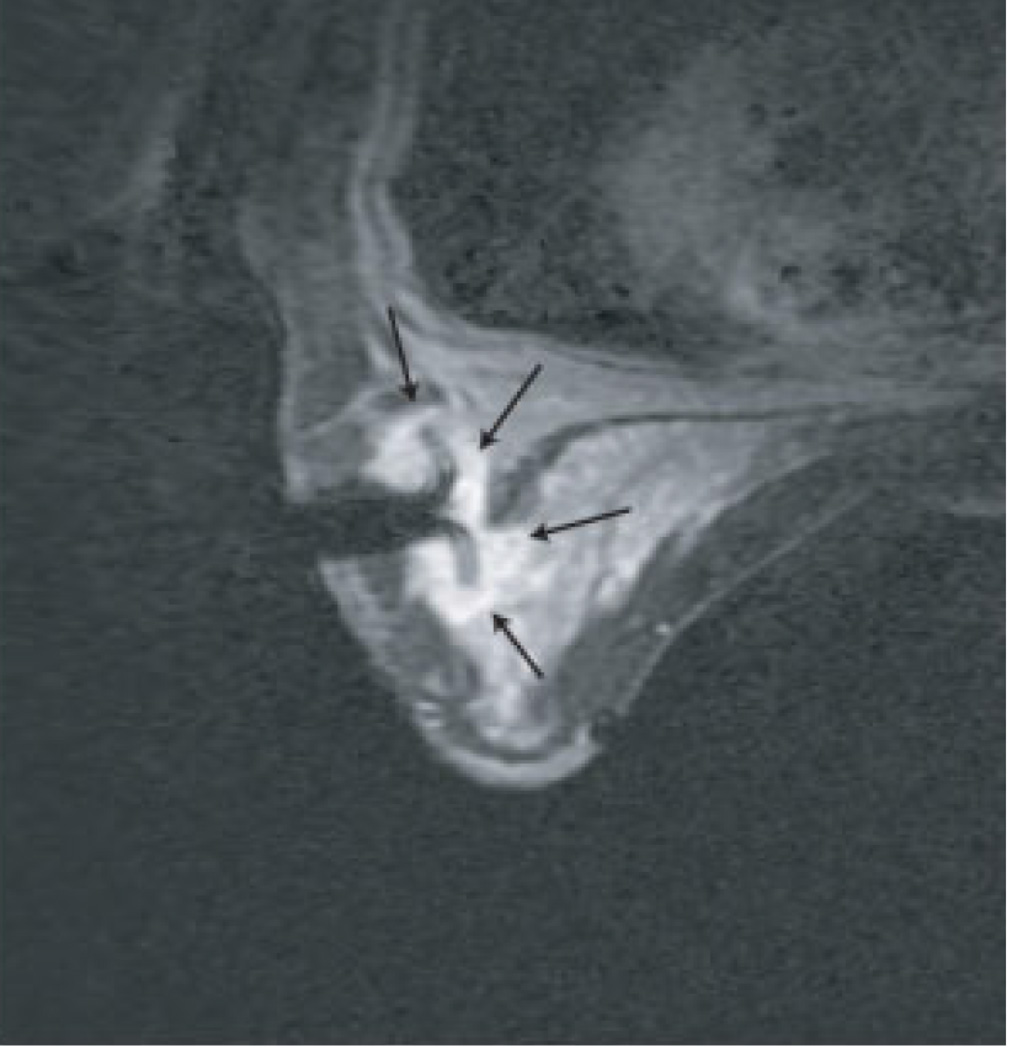
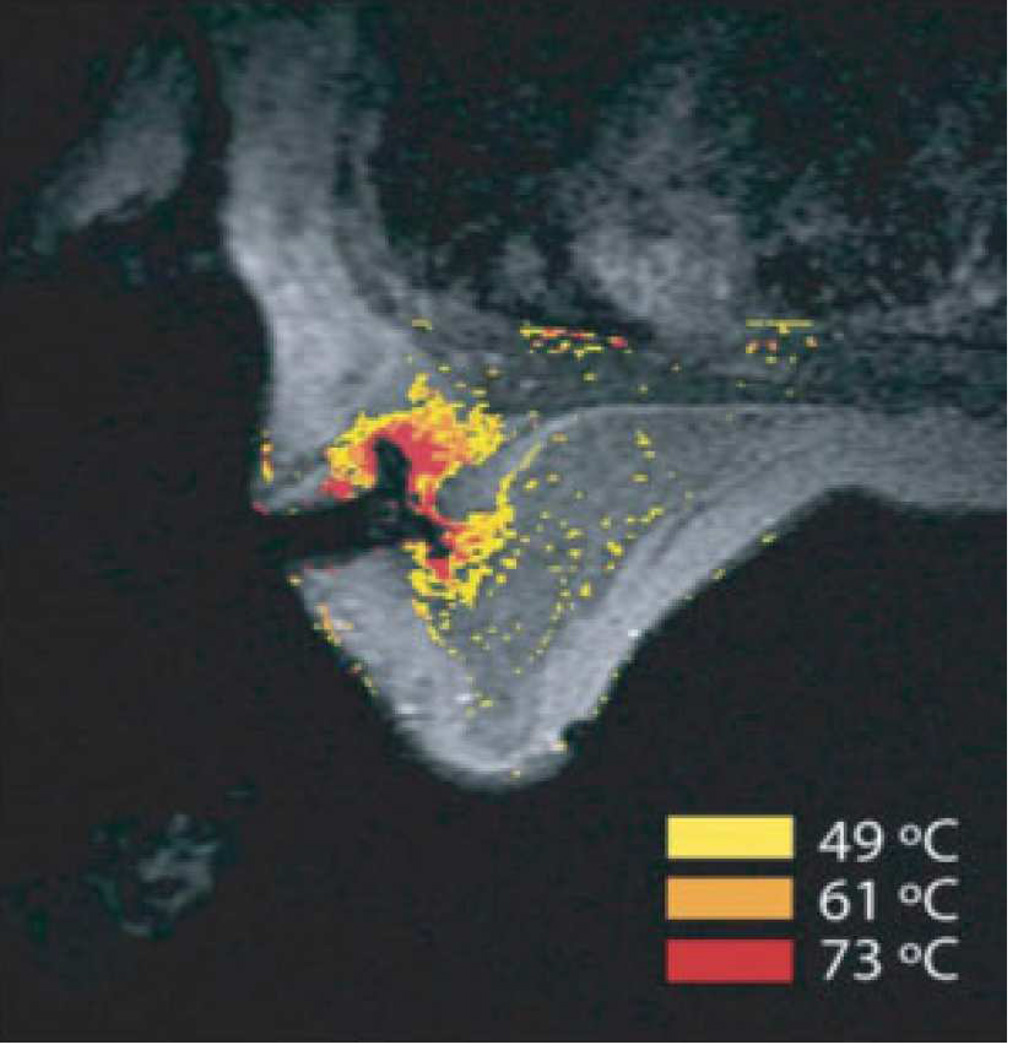
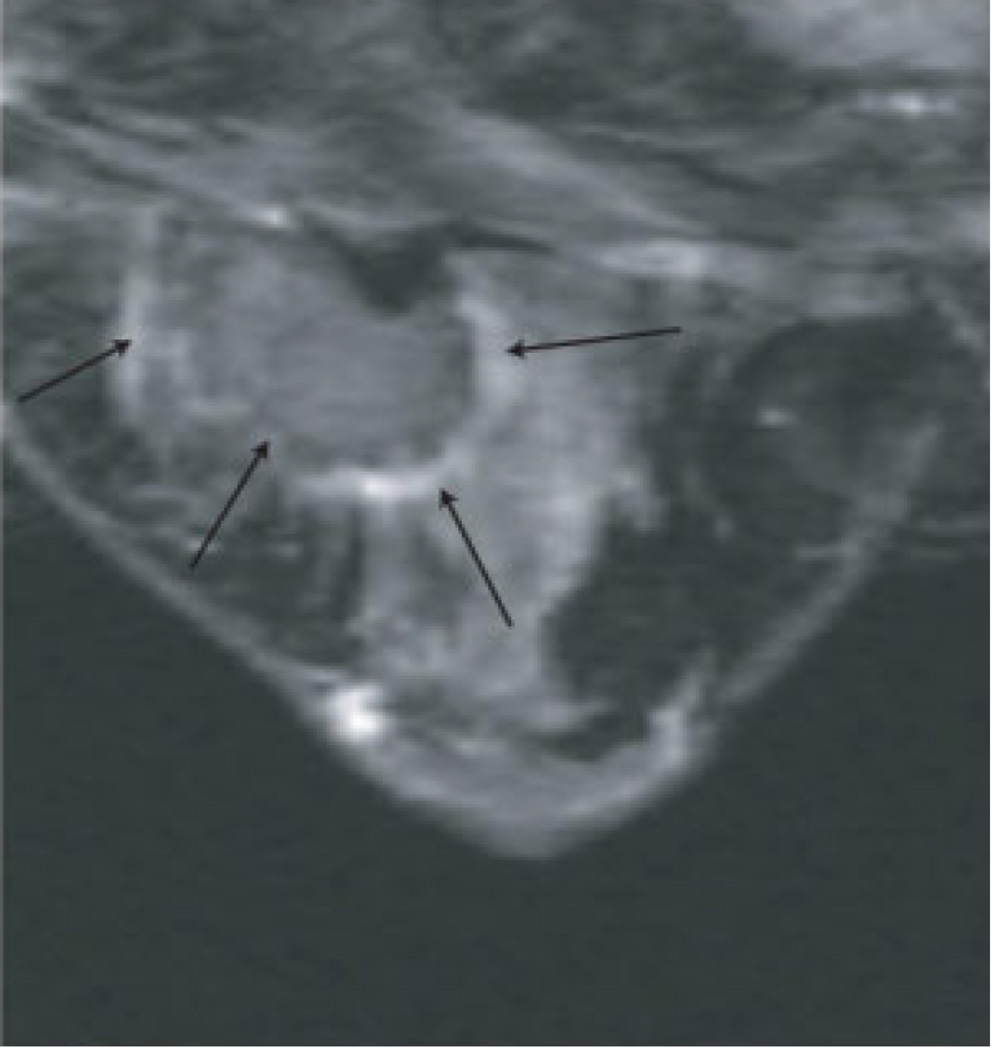
Figure 5. MRI-guided RF ablation.
Contrast-enhanced three-point Dixon gradient-echo images with patient in prone position showing the fully deployed LeVeen needle electrode (signal void) centrally in the enhancing tumor mass (arrows) in the right breast (A). Same axial positioning showing the magnetic resonance PRF shift thermomap (yellow zone 49 °C, orange 61 °C, red 73 °C) around the deployed RFA electrode centrally in the mass (B). Post-procedure contrast-enhanced water-selective, spectral-spatial [AU11] FSE image of the right breast demonstrates a small enhancing rim representing the border of the ablation zone corresponding to fresh scar tissue (C) (arrows).
(From van den Bosch et al. MRI-guided radiofrequency ablation of breast cancer: preliminary clinical experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008;27(1):204–208, with permission.)