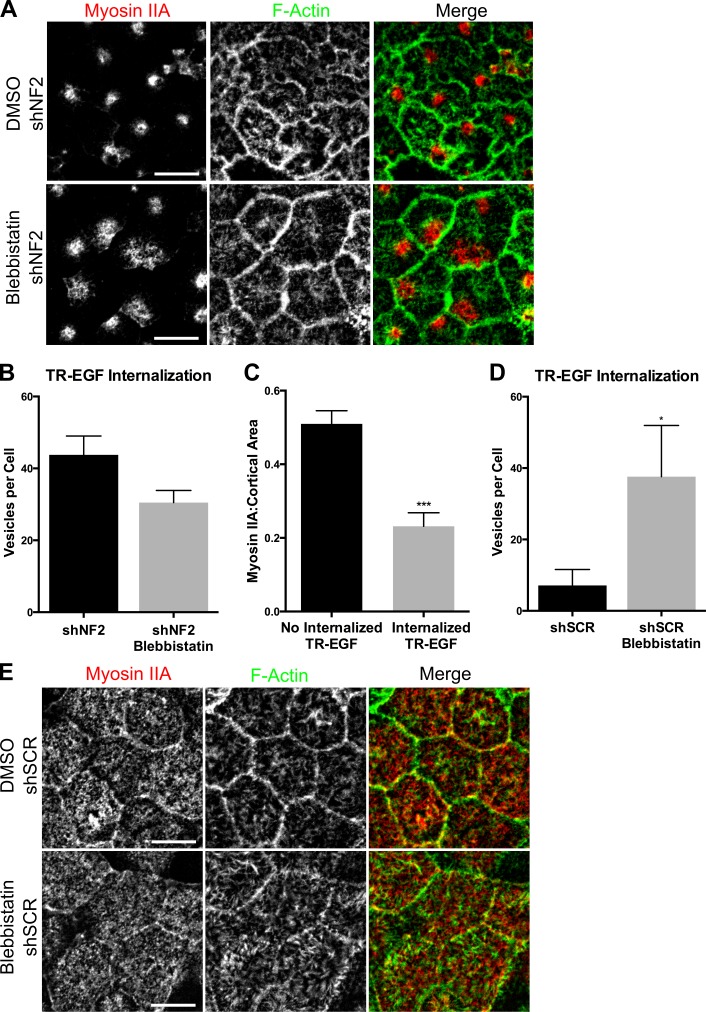
Figure 6.
Uniformly distributed MyoIIA is essential for contact-dependent inhibition of EGFR internalization. (A) Confocal images of shNF2-expressing cells treated with 100-µM blebbistatin or DMSO and stained for MyoIIA and F-actin. (B) Quantification of internalized TR-EGF–containing vesicles (30 min after stimulation) in DMSO and blebbistatin-treated shNF2-expressing cells. n = >50 cells per group. P > 0.05. (C) Graph shows the fraction of cortical area covered by MyoIIA in shSCR cells that do not (left) versus do (right) display internalized TR-EGF at 30 min after stimulation. n = 25 cells per group. (D) Internalized TR-EGF (30 min after stimulation) was quantified in DMSO and blebbistatin-treated control cells. n = >50 cells per group. (E) Confocal images depict MyoIIA and junctional F-actin localization in control Caco2 cells treated with DMSO or 100-µM blebbistatin. Error bars indicate SEM. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. Data are representative of at least three experiments. Bars, 10 µm.