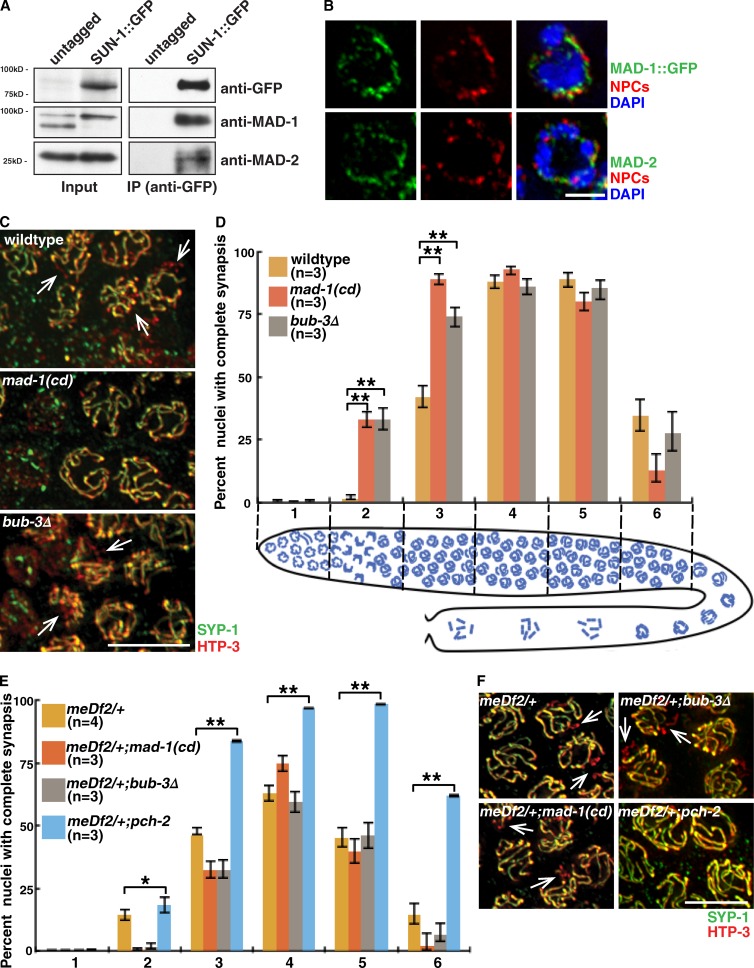
Figure 2.
SAC proteins interact with PC-associated protein SUN-1, localize to the periphery of meiotic nuclei, and inhibit synapsis in a PC-dependent manner. (A) MAD-1 and MAD-2 coimmunoprecipitate with SUN-1::GFP. Lysates and IPs from untagged and tagged worm strains blotted with antibodies against GFP, MAD-1, and MAD-2. (B) MAD-1::GFP and MAD-2 are at the nuclear periphery marked with NPCs. Images of partial projections of meiotic nuclei stained to visualize DNA (blue), MAD-1::GFP or MAD-2, and NPCs. (C) Images of nuclei during synapsis initiation in wild-type worms and mad-1(cd) and bub-3Δ mutants stained to visualize SYP-1 and HTP-3. (D) mad-1(cd) and bub-3Δ mutants accelerate synapsis. Cartoon depicts worm germline. Meiotic progression is from left to right. (E) Mutation of mad-1 or bub-3 does not accelerate synapsis in meDf2/+. (F) Mutation of mad-1 or bub-3 does not rescue the synapsis defect in meDf2/+. Images of nuclei in meDf2/+, meDf2/+;mad-1(cd), meDf2/+;bub-3Δ, and meDf2/+;pch-2 mutants stained to visualize SYP-1 and HTP-3. (C and F) Arrows indicate unsynapsed chromosomes. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.0001 in all graphs. Bars: (B) 2 µm; (C and F) 5 µm.