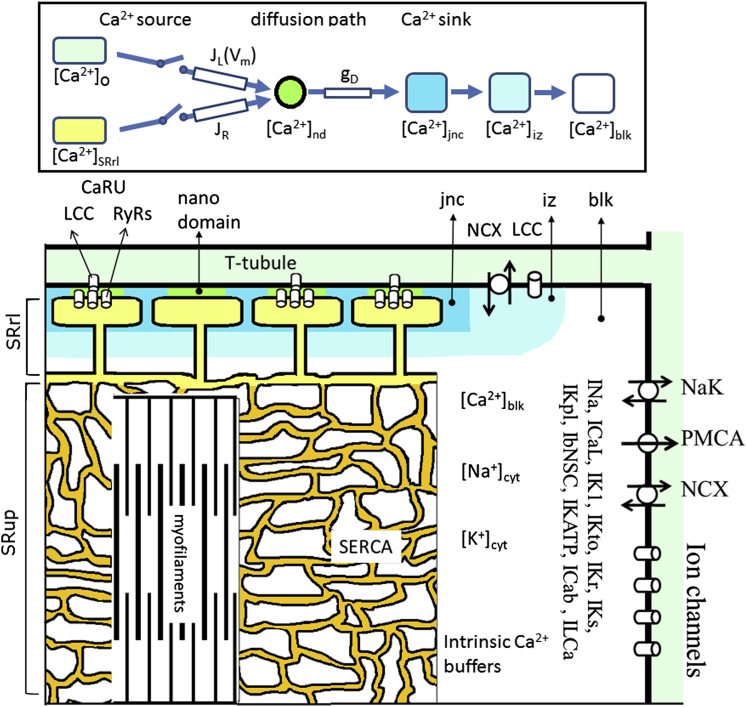
Figure 1.
Composition of the HuVEC model demonstrated by a half-sarcomere. The compartments of jnc, iz, and blk in the cytosol, SR, and T-tubule are filled with different colors. The ion channels and transporters are located on the sarcolemma, SERCA and RyRs are on the SR membrane, and the contractile fibers are in blk. A single CaRU consists of a hypothetical LCC and a couplon in the junctional cleft (filled with green color), and individual CaRUs are spatially separated from their neighbors by jnc. The inset at the top shows a schematic presentation of the diffusion pathway of Ca2+ from the Ca2+ sources to the sink. JL, JR, and gD represent the permeability of single LCCs and RyRs, and the Ca2+ flux rate from nd to jnc, respectively. The myofilaments were embedded in an SR network (SRup). ICaL: L-type Ca2+ current; INa: sum of Na+ currents in transient and late modes; INaT + INaL; IK1: inward rectifier K+ current; IKr: rapid component of delayed rectifier K+ current; IKs: slow component of delayed rectifier K+ current; IKto: transient outward K+ current; IKpl: plateau K+ current; Il(Ca): Ca2+-activated background cation current; ICab: background Ca2+ current; IKATP: ATP-sensitive K+ current; IbNSC: background nonselective cation current; NaK: Na+/K+ pump; NCX: Na+/Ca2+ exchanger; PMCA: plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase; SERCA: sarco-/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump.