Figure 1.
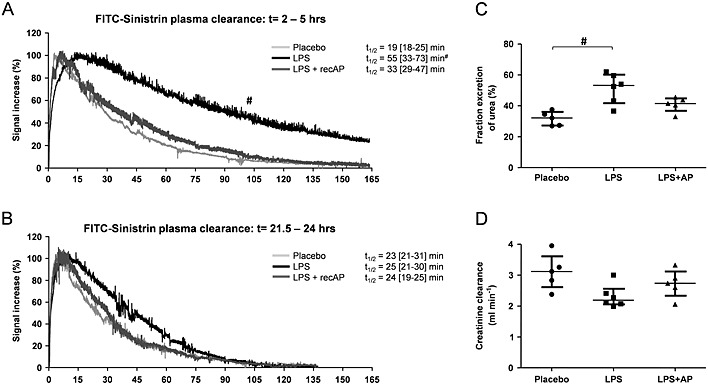
RecAP prevents the LPS‐induced deterioration in renal function in vivo. Renal function was assessed by the transcutaneous measurement of FITC‐sinistrin t 1/2. AKI was induced in rats by LPS (0.3 mg kg−1 BW, t = 0 h), followed by recAP treatment (1000 U kg−1 BW) at t = 2. The t 1/2 measurements were performed at t = 2 h and t = 21.5 h (A, B: examples of FITC‐sinistrin kinetics obtained for one rat at the two respective time points). Urine was collected between t = 5 and t = 16 h, and plasma was sampled at t = 1.5 and t = 24 h, allowing calculation of (C) fractional urea excretion and (D) creatinine clearance with the average plasma value of t = 1.5 and t = 24 h. Data are expressed as median [25th percentile, 75th percentile] (Placebo, LPS n = 6; LPS + recAP n = 5), # P < 0.05 compared with placebo. RecAP, recombinant alkaline phosphatase; AKI, acute kidney injury.
