Figure 1.
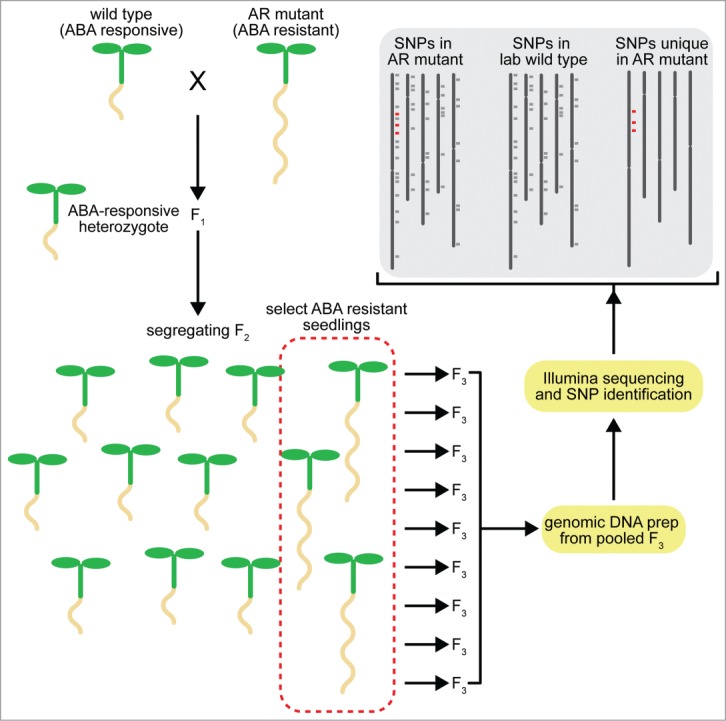
Scheme for identifying potential causative mutations in Arabidopsis with NGS. In this example, we cross an ABA-resistant (AR) mutant created by ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) treatment to wild type (Columbia-0). The resultant F1 is self-pollinated to create a segregating F2 population. Individuals displaying the phenotype of interest (ABA resistance in root elongation) are selected and allowed to self-pollinate to create F3 progeny. These progeny are retested for the phenotype of interest, tissue from multiple retested F3 lines are pooled, and bulk genomic DNA is sequenced using Illumina technology. The resulting reads are aligned to the reference sequence (TAIR v10) using Novoalign (Novocraft; http://novocraft.com) and SNPs identified by SAMtools20 and annotated using snpEFF.21 We then compare identified canonical EMS-induced changes (G-to-A or C-to-T) from our mutant to our lab wild type Col-0 strain to identify mutations unique to the mutant.
