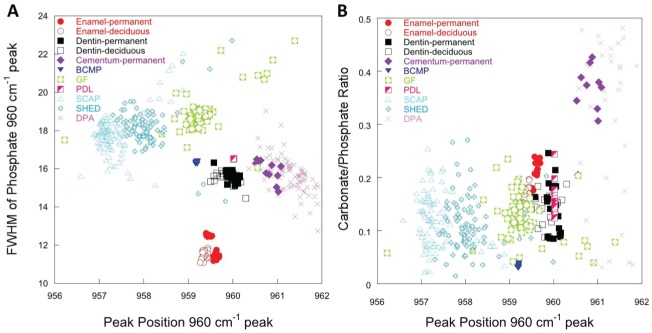
Figure 4.
Component analysis plots for native dental tissues and material formed by dental stem cells. (A) Characteristic full-width half maximum of the phosphate PO43- ν1 stretching modes as a function of the peak position of the same for the mineral components of native enamel, dentin, and cementum, as well as BCMP, GF, PDL, SCAP, SHED, and DPA. Strong overlaps in these mineral variables correspond to correlations in the stress state and crystallinity in the native tissues and mineral deposits. Nodules from PDL and BCMP correlated strongly with native dentin, while those from DPA corresponded to that of native cementum. (B) Carbonate substitution calculated by measuring the area under the CO32- ν1 with respect to the area under the PO43- ν1 mode is plotted as a function of the position of the PO43- ν1 mode. Native dentin, native enamel, SCAP, SHED, GF, and PDL all produce similar levels of carbonate substitution, while DPA and native cementum produce somewhat higher levels. BCMP, bone chip mass population; DPA, dental pulp adult; GF, gingival fibroblast; PDL, periodontal ligament; SCAP, stem cells from apical papilla; SHED, stem cells from human-exfoliated deciduous teeth.