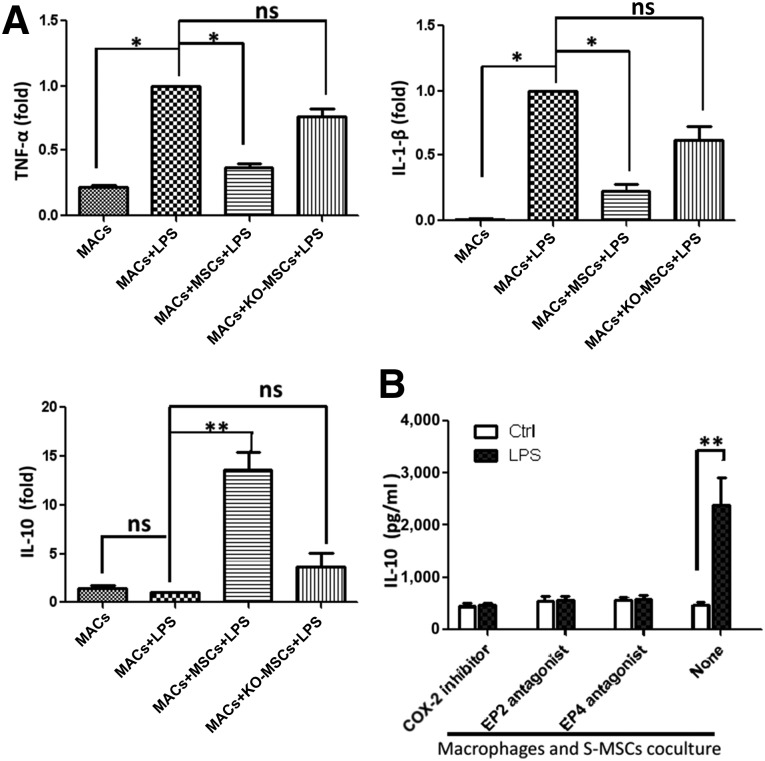
Figure 5.
S-MSCs inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines and enhance the production of IL-10 by LPS-induced MACs via PGE2. MACs were cultured overnight in the absence or presence of S-MSCs or KO-MSCs (MACs: S-MSCs or KO-MSCs ratio = 10:1). (A): Cells were then washed and incubated for 6 hours with or without LPS (100 ng/ml), and cytokines were analyzed in cells by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Effect of the indomethacin (COX-1/2 inhibitor; 5 µM), A6809 (EP2 receptor antagonist; 10 µM), and GW627368X (EP4 receptor antagonist; 10 µM) on the LPS-induced IL-10 release in MAC and S-MSC cocultures. Cell cocultures pretreated with COX-2 inhibitor or EP2/EP4 antagonist or medium (none) for 30 minutes were stimulated with or without LPS (100 ng/ml) for an additional 12 hours. (B): The production of IL-10 was analyzed in supernatants of cocultures by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All results shown are representative of the arithmetic mean ± SEM of six independent experiments. ∗, p < .05, ∗∗, p < .01, versus MACs plus LPS. Abbreviations: COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; Ctrl, control; IL-1β, interleukin 1-β; IL-10, interleukin-10; KO-MSC, NF-κB−/−-skin-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment group; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAC, macrophage; MSC, skin-derived mesenchymal stem cell; ns, nonsignificant; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.