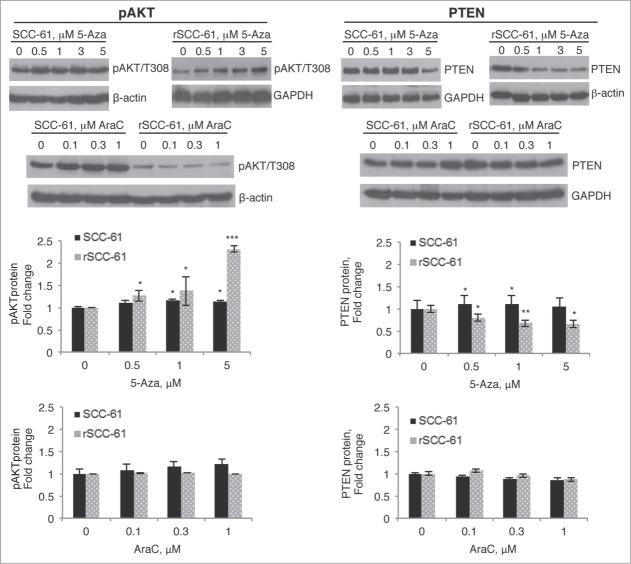
Figure 6.
Treatment of rSCC-61 cells with 5-Aza decreases PTEN levels and upregulates downstream AKT signaling. SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells were treated with 0–5 µM 5-Aza or 0–1 µM AraC for 4 days. Cells were then lysed for Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies for monitoring AKT phosphorylation (A) and PTEN expression (B). Treatment of rSCC-61 cells with 5-Aza induced an increase in AKT phosphorylation and a decrease in PTEN expression independent of its cytotoxic effects seen in AraC control experiments. Quantification of the Western blots is shown from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant changes in pAKT or PTEN at each 5-Aza or AraC concentration relative to the untreated rSCC-61 and SCC-61 cells, respectively [α = 0.05, P-values of 0.01–0.05 (*), 0.001–0.01 (**), or <0.001 (***)].