Figure 6.
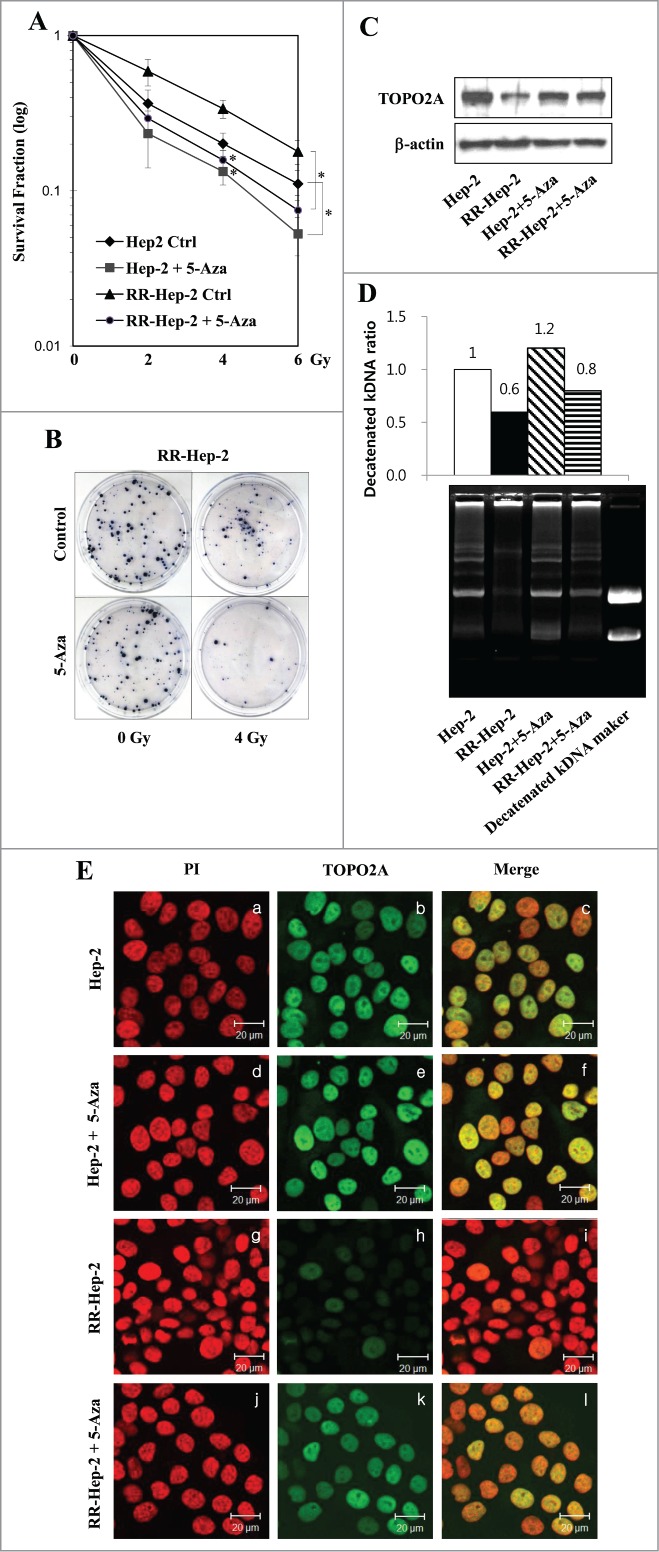
The 5-Aza-mediated induction of TOPO2A reduces the survival of Hep-2 and RR-Hep-2 cells and increases TOPO2A activity. (A) Hep-2 and RR-Hep-2 cells were treated with or without 5-Aza (5 μM), and clonogenic survival fractions were determined following exposure to the indicated doses of radiation. (B) RR-Hep-2 cells were treated with 5-Aza (5 μM) and then further treated with or without 4-Gy irradiation. Colony formation was visualized by trypan blue staining. (C) The protein levels of TOPO2A were determined by Western blotting; β-actin was employed as the loading control. (D) TOPO2A decatenation activity was measured in nuclear extracts from Hep-2 and RR-Hep-2 cells treated with or without 5 μM of 5-Aza for 72 h. (E) Hep-2 and RR-Hep-2 cells were treated with or without 5-Aza (5 μM) for 72 h and fixed with 4% (v/v) paraformaldehyde. Cells were stained for TOPO2A using an FITC-conjugated secondary antibody, and propidium iodide (PtdIns) was used to visualize nuclei. Panels: (a, d, g, and j) PI (red) staining; (b, e, h, and k) localization of TOPO2A (green); and (c, f, i and l) merged images of TOPO2A and PtdIns. The data presented represent a typical result or average values with standard deviations from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05.
