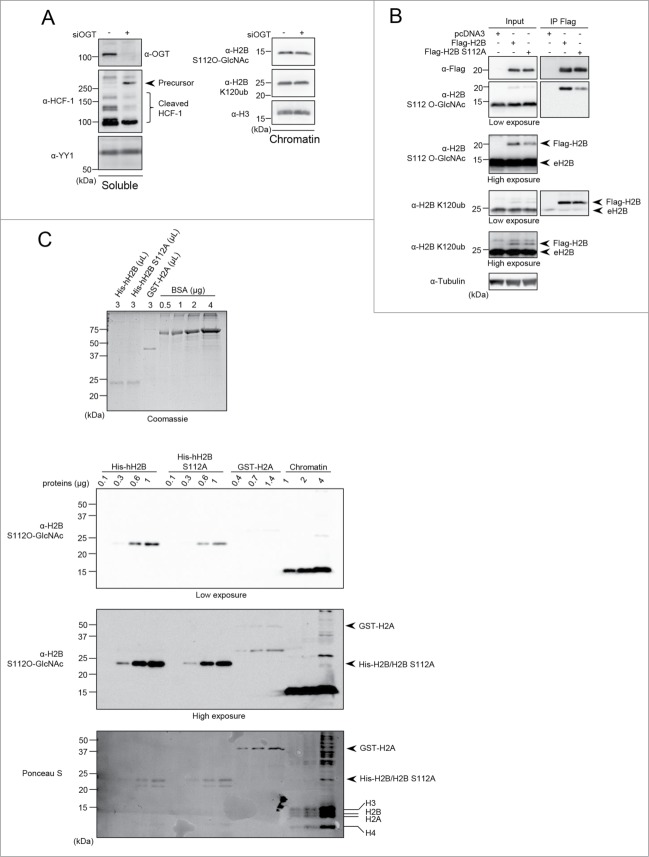
Figure 5.
(See previous page). H2B S112 O-GlcNAc antibody is not specific and S112 O-GlcNAcylation is not linked to H2B K120 monoubiquitination. (A) HeLa cells were transfected twice with OGT siRNA and three days posttransfection, cells were harvested to perform cellular fractionation. Protein levels were analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. HeLa soluble fraction was analyzed for HCF-1 proteolytic cleavage. YY1 was used as a loading control (Left panel). Chromatin fraction was analyzed for H2B S112 O-GlcNAc and H2B K120ub levels (Right panel). (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-H2B or Flag-H2B S112A. Three days posttransfection, cells were harvested and total cell lysates were subjected to protein denaturation and immunoprecipitation (IP) using α-Flag antibody. Input as well as IP fractions were subjected to immunoblotting analysis using the indicated antibodies. Arrows indicate Flag-H2B and endogenous H2B (eH2B). Tubulin was used as a loading control for the input fraction. (C) Relative quantification of eluted purified recombinant histones detected by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. Known amounts of BSA protein were used as standards for relative quantification (Top panel). Increasing amounts of recombinant His-hH2B, His-hH2B S112A mutant, GST-H2A as well as chromatin extract from HEK293T cells were analyzed by western blot using the indicated antibodies. Red Ponceau S staining of the membrane used for subsequent western blotting showing the loading of purified proteins (Bottom panel). Arrows and lines indicate the position of recombinant and endogenous histones respectively. kDa: Molecular weight marker in kilodalton.