Figure 6.
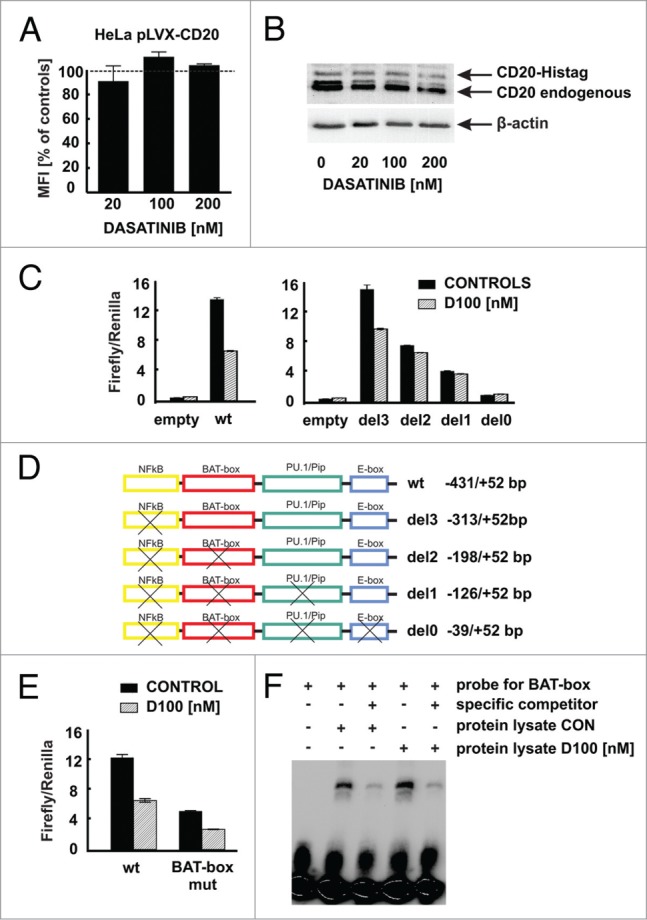
Modulation of CD20 expression by dasatinib requires CD20 promoter. (A) HeLa cells stably transduced to express CD20 (HeLa pLVX-CD20-IRES-PURO) were incubated for 48 h with increasing concentrations of dasatinib. Surface CD20 levels were determined as described earlier. (B) Protein lysates from Raji cells modified to express CD20-Histag fusion protein pre-incubated for 48 h with increasing concentrations of dasatinib were separated in polyacrylamide gel. CD20 and CD20-Histag proteins were detected with anti-CD20 antibody. (C) Relative luciferase activity was measured in lysates from Raji cells transfected with either empty vector or pGL4-wild type CD20 promoter or with pGL4-truncated CD20 promoters and further incubated with dasatinib (100 nM) for subsequent 24 h. (D) Scheme of truncated CD20 promoters used for reporter assays. (E) Relative luciferase activity was measured in lysates from Raji cells transfected with either pGL4-wild type or mutated (BAT-box mut) CD20 promoters incubated with dasatinib (100 nM) for subsequent 24 h. (F) Nuclear lysates from Raji cells either control or incubated for 24 h with dasatinib (100 nM) were mixed with biotinylated BAT-box probe in presence or absence of specific competitor. Formed DNA-protein complexes were analyzed for the binding of the proteins to the putative Oct-2 binding site in the CD20 promoter. Shown is one representative of at least 2 independent experiments.
