Figure 4.
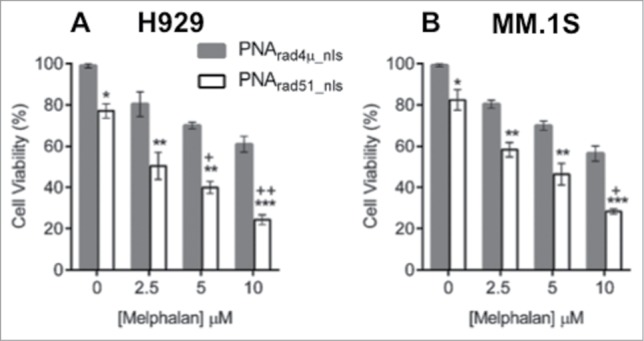
PNA targeting RAD51 inhibits myeloma cell growth and sensitizes MM cells to melphalan in vitro. (A, B) Cell viability of H929 (A) and MM.1S (B) cell lines was measured by WST-1 assay after cells were treated as described in “Materials and Methods.” The data represent mean ± SEM of triplicate samples in each of 3 independent experiments, each considered as a single point (i.e. considering only the biological N of 3). Viability of PNArad4μ_nls was set to 100%, and other treatments expressed relative to that value. *, ** and *** indicate P < 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001, respectively, for the indicated PNArad51_nls bar relative to the corresponding PNArad4μ_nls control, at each melphalan exposure (0, 2.5, 5 or 10 µM) indicated on the x-axis. Significance of synergy was calculated by a 1-tailed, heteroscedastic t test comparing the normalized cell viability obtained with PNArad51_nls plus melphalan (a%) with the product of the survival fractions for each agent administered separately (i.e., comparing a% to d% = b% × c%). + and ++ indicate P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively, for significance of synergy between the observed viability inhibition with the PNArad51_nls plus melphalan combination, relative to the loss of viability expected from the product of their individual survival fractions.
