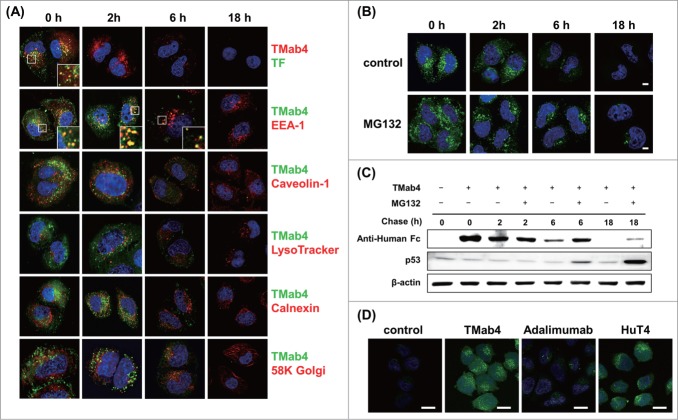
Figure 4.
Intracellular trafficking and cytosolic release of internalized TMab4. (A) Pulse-chase intracellular trafficking of internalized TMab4 monitored by co-localization with TF, early endosome marker EEA-1, caveolin-1, late endosome/lysosome marker LysoTracker, ER marker calnexin, or Golgi marker 58K Golgi protein, as visualized by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Insets, enlarged images of the regions in the boxes. (B and C) Intracellular stability of internalized TMab4 with or without the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (30 μM) was analyzed by confocal microscopy (B) and western blotting (C). HeLa cells were pulsed with 3 μM of TMab4 for 30 min and incubated for the indicated times in the presence or absence of MG132 (30 μM) prior to analysis. In (B), TMab4 was visualized with FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG Fc antibody (green). In (C), equal amounts of cell lysates were loaded, and retained TMab4 was detected by protein gel blotting, using p53 as a positive control (revealing proteasome-involved degradation) and β-actin as a loading control. In (A–B): magnification, 630×; scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Cytotransmab-mediated cytosolic release of calcein. HeLa cells were untreated (′control′) or treated with 5 μM of TMab4, adalimumab, or HuT4 for 4 h and then incubated with 50 μM of calcein for additional 2 h at 37°C, followed by confocal analysis. Image magnification, 630×; scale bar, 20 μm. In (A, B, and D), images show the merging of markers/antibodies (indicated colors) and Hochest33342-stained nuclei (blue) at the centered single confocal section.