Figure 1.
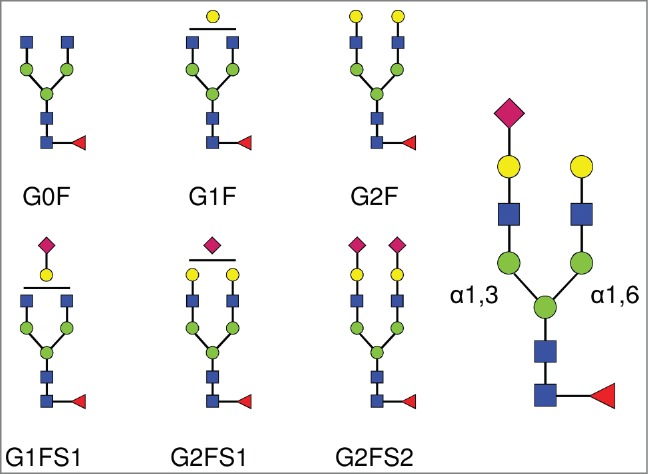
Complex biantennary N-linked glycan structures found in the Fc domain of IgGs. All complex glycans are composed of 4 N-acetylglucosamine residues (GlcNAc, blue squares), and 3 mannose residues (green circles). G0, G1, G2 indicate 0, 1 or 2 galactose residues (yellow circles). F indicates the presence of a core-fucose residue (red triangle). S1 and S2 indicate mono- and di-sialylated glycans (sialic acids are represented as purple diamonds). The sialic acid linkage type is indicated when required in parentheses: G1FS(3)1 and G1FS(6)1 designate G1FS1 carrying either a α2,3- or a α2,6-linked sialic acid, respectively. Similarly, G2FS1 may be G2FS(3)1 or G2FS(6)1. G2FS(3,3)2, G2FS(3,6)2 and G2FS(6,6)2 designate G2FS2 carrying 2 α2,3SA, one α2,3SA and one α2,6SA, or 2 α2,6SA, respectively. α1,3 and α1,6 designate the linkage types of the core mannose residues, and by extension refer to the branches initiated by these residues: the α1,3-arm and the α1,6-arm, respectively.
