Figure 1.
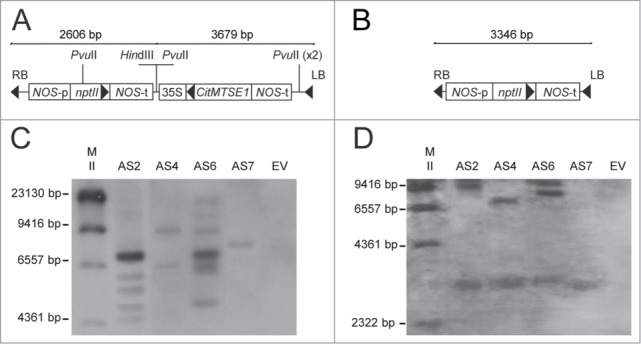
Molecular analysis of DNA isolated from orange leaves of antisense (AS) and empty vector control (EV) Navelina sweet orange transgenic plants. (A, B) Map of the T-DNA region of the binary vector used to transform AS (A) and EV (B) plants. LB, left T-DNA border region; RB, right T-DNA border region; nptII, neomycin phosphotransferase II transgene conferring kanamycin resistance, under the control of the nopaline synthase (NOS) promoter and terminator regions; CitMTSE1, limonene synthase gene in antisense orientation under control of the Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter and the NOS terminator. (C, D) Southern blot analysis of independent AS transgenic lines (AS2, AS4 and AS6 and AS7) and the EV control line. The DNA was digested with the enzymes HindIII for testing loci number integrations (C) or PvuII for assessing integrity of the D-limonene transgene (D). The 35S promoter was used as a probe. M: DNA molecular weight marker II from Roche Applied Science.
