Figure 3.
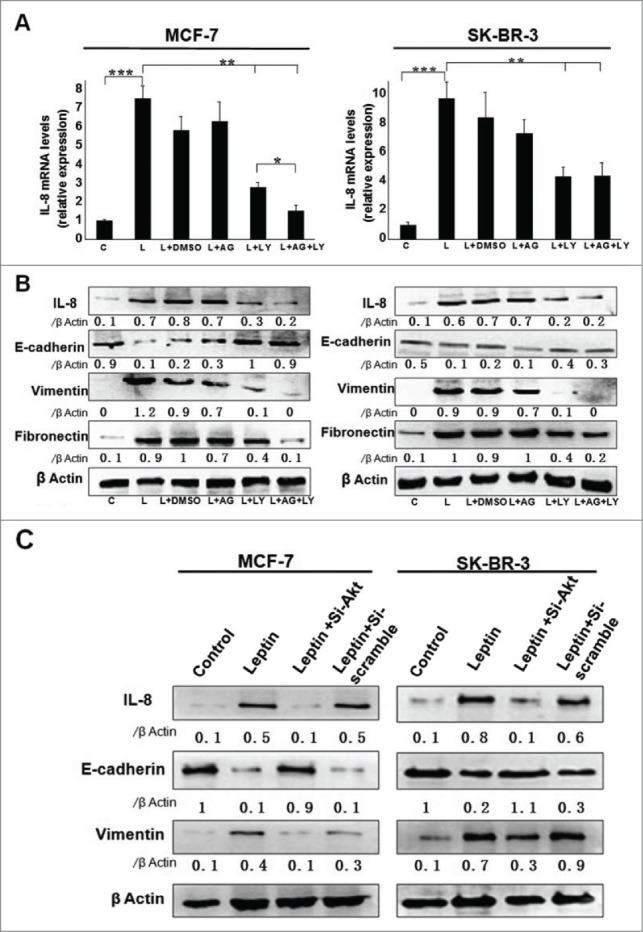
Leptin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells were abolished in the presence of AKT inhibitor and monoclonal Ab against IL-8. Serum-starved MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells were pretreated with 50 μM AG490 or 20 μM LY294002 for 1 h followed by 100 ng/ml leptin treatment for 24 h, DMSO were added as control. For IL-8 blocking experiments, specific antibodies to IL-8 or control IgG were added in serum-starved MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells cultures together with leptin and then incubated for 48 h. (A) QPCR and (B) Western blotting analysis indicated that LY294002 could abolish leptin-induced activation of IL-8 of MCF-7, SK-BR-3 cells (P < 0.05). (B) Western blotting analysis indicated that LY294002 could also restore the changes of Vimentin, Fibronectin and E-cadherin achieved by leptin treatment. (C)Western blotting analysis indicated that Akt depletion using Akt-siRNA could also restore the changes of IL-8, Vimentin and E-cadherin achieved by leptin treatment compared with nontargeting control siRNA. (D)Western blotting and (E) Immunofluorescence assay with Fluorescent confocal microscopy showed that comparing with control IgG, IL-8 specific antibody could completely abolish the hallmarks of leptin-induced EMT of MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells (P < 0.05).(F)Cell scratch assay and (G)Transwell chamber showed that leptin obviously advanced the migration and invasion capability of MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells after 36 h incubation, respectively. While IL-8 antibody could reduce the effects compared with control Ab (P < 0.05). Original magnification: ×200.
Figure 3.
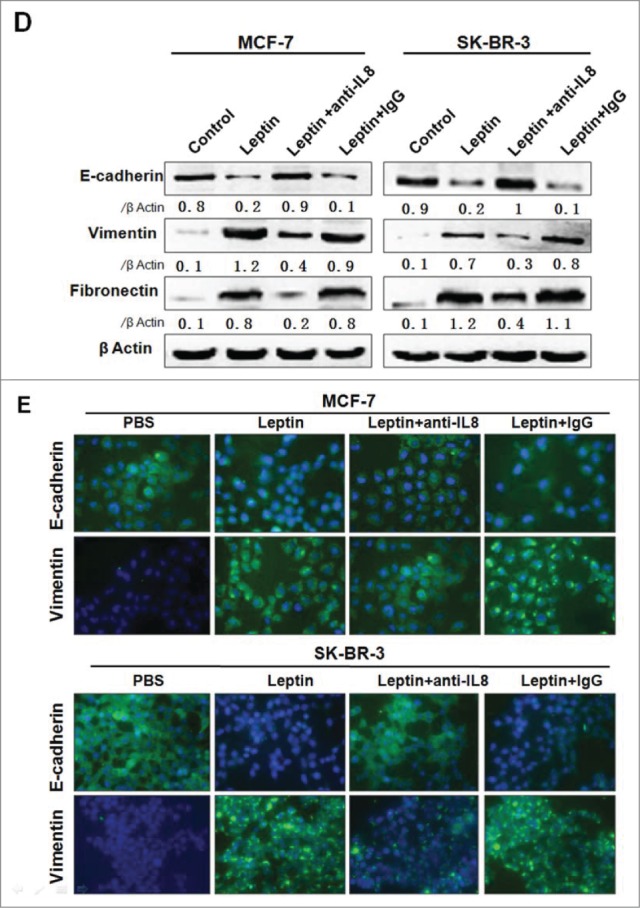
(Continued)
Figure 3.
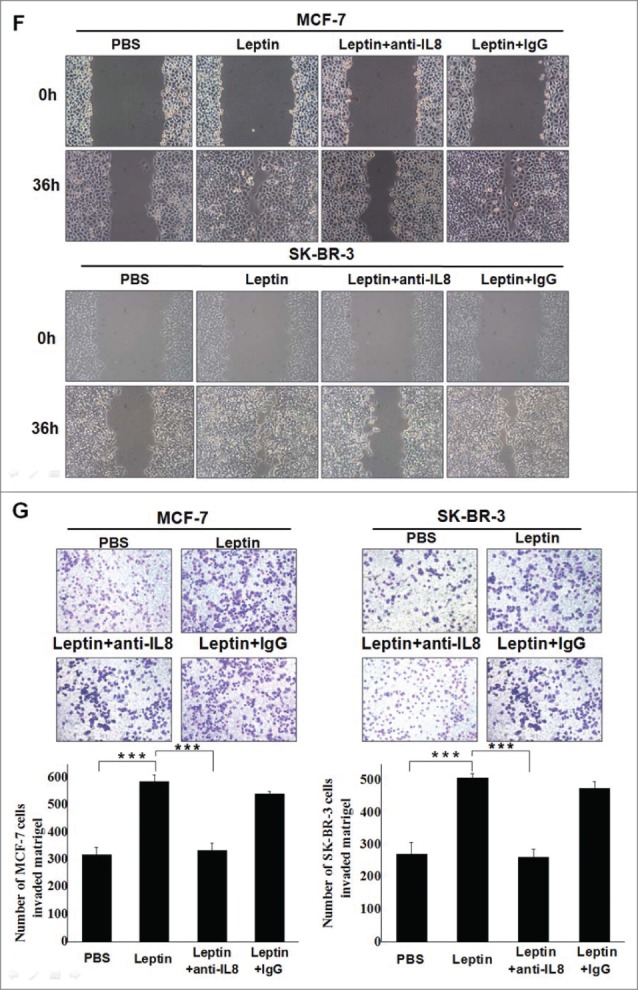
(Continued)
